Co-Encapsulation of Drugs for Topical Application-A Review
- PMID: 36771111
- PMCID: PMC9921006
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28031449
Co-Encapsulation of Drugs for Topical Application-A Review
Abstract
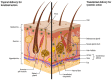
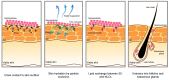
Achieving the best possible outcome for the therapy is the main goal of a medicine. Therefore, nanocarriers and co-delivery strategies were invented to meet this need, as they can benefit many diseases. This approach was applied specifically for cancer treatment, with some success. However, these strategies may benefit many other clinical issues. Skin is the largest and most exposed organ of the human body, with physiological and psychological properties. Due to its exposition and importance, it is not difficult to understand how many skin diseases may impact on patients' lives, representing an important burden for society. Thus, this review aims to summarize the state of the art in research concerning nanocarriers and co-delivery strategies for topical agents' applications targeting skin diseases. The challenge for the medicine of the future is to deliver the drug with spatial and temporal control. Therefore, the co-encapsulation of drugs and the appropriate form of administration for them are so important and remain as unmet needs.
Keywords: co-encapsulation; nanoparticles; skin barrier; topical delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Richard M.A., Paul C., Nijsten T., Gisondi P., Salavastru C., Taieb C., Trakatelli M., Puig L., Stratigos A., EADV Burden of Skin Diseases Project Team Prevalence of most common skin diseases in Europe: A population-based study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022;36:1088–1096. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18050. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical