Ongoing Treatment with a Spore-Based Probiotic Containing Five Strains of Bacillus Improves Outcomes of Mild COVID-19
- PMID: 36771194
- PMCID: PMC9920365
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15030488
Ongoing Treatment with a Spore-Based Probiotic Containing Five Strains of Bacillus Improves Outcomes of Mild COVID-19
Abstract
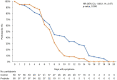
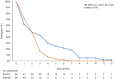
Spore-based Bacillus probiotic treatment improves intestinal health. The intestinal microbiota influences both the innate and adaptive immune responses. As such, the influence of ongoing spore-based probiotic treatment (five probiotic strains of Bacillus) on the clinical outcomes of mild COVID-19 was evaluated in this retrospective, observational study. Demographics, medical history, probiotic use, and COVID-19 symptom information were collected. The study included 120 patients with a PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild COVID-19 symptoms. The probiotic group (n = 60) comprised patients with ongoing probiotic treatment (≥1 month); the control group comprised patients not taking probiotics (n = 60). The primary outcome was time to symptom resolution; secondary outcomes included time to fever resolution and presence of digestive symptoms. The probiotic group had a significantly shorter time to symptom resolution (mean (95% confidence interval) days: control group, 8.48 (6.56, 10.05); probiotic group, 6.63 (5.56; 6.63); p = 0.003) and resolution of fever (control group, 2.67 (1.58, 3.61); probiotic group, 1.48 (1.21, 2.03); p < 0.001). More patients in the probiotic group (n = 53) than in the control group (n = 34) did not have digestive symptoms (p < 0.001). Among adults with mild COVID-19, participants receiving ongoing probiotic treatment had a shorter clinical course, and fewer had digestive symptoms compared with those not taking probiotics.
Keywords: Bacillus; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; fever in COVID-19 infection; gastrointestinal COVID-19 symptoms; gut microbiota; gut–lung axis; immunomodulation; probiotics; time to symptom resolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 16 January 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/#:~:text=Globally%2C%20as%20of%204%3A54pm,vaccin....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

