Immunonutrition in Orthopedic and Traumatic Patients
- PMID: 36771245
- PMCID: PMC9919811
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15030537
Immunonutrition in Orthopedic and Traumatic Patients
Abstract
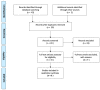
The role of nutrition intervention in surgical settings is constantly developing and evolving. Immunonutrition represents a viable option to reduce perioperative and postoperative complications in surgical oncology. However, as far as we know, little research has been conducted in the orthopedic field. With this review, we aim to summarize the state of the art in the application of immune-enhanced compounds to surgical, orthopedic, and traumatic patients. The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines were adopted. A comprehensive search was carried out using the PubMed (MEDLINE), EMBASE, and Cochrane Library databases. All the studies dealing with immunonutrition fed to traumatic and orthopedic patients were pooled, the data were extracted, and the studies were discussed. A total of eight studies were included: six focused on trauma surgery and two on elective orthopedic surgery. The epidemiological characteristics of participants and the assessment of results were reported. Data were analyzed using R software (2020; R Core Team). Based on the current available literature, a positive impact of immunonutrition in orthopedic and trauma surgical settings was registered. All studies analyzed showed the favorable impact of the immunonutrition diet on clinical outcomes. The full effect of this type of nutrition and its different applications in the orthopedic and traumatic fields should be critically investigated through more extensive randomized controlled trials.
Keywords: immunonutrition; nutrition; orthopedics; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of enteral immunonutrition and enteral nutrition in patients undergoing gastric cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials.J Int Med Res. 2024 Jan;52(1):3000605231220870. doi: 10.1177/03000605231220870. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38179793 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of perioperative immunonutrition on outcomes in gastric cancer surgery patients: A systematic review and evidence map.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025 Jun;67:90-104. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.02.029. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025. PMID: 40074199
-
Impact of perioperative immunonutrition on postoperative outcomes in pancreaticoduodenectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 16;24(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03510-6. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39550568 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative immunonutrition in esophageal cancer patients undergoing esophagectomy: the first meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Dis Esophagus. 2020 Apr 15;33(4):doz111. doi: 10.1093/dote/doz111. Dis Esophagus. 2020. PMID: 31950146 Review.
-
Is immunonutrition superior to standard enteral nutrition in reducing postoperative complications in patients undergoing esophagectomy? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J BUON. 2021 Jan-Feb;26(1):204-210. J BUON. 2021. PMID: 33721453
Cited by
-
Current Trend and Outcomes on Immunonutrition in Medical and Surgical Fields: An Updated Perspective.Malays J Med Sci. 2024 Dec;31(6):65-76. doi: 10.21315/mjms2024.31.6.6. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Malays J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39830099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Patient Perceptions of Nutrition in the Perioperative Episode of Care.Arthroplast Today. 2025 Mar 3;32:101646. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2025.101646. eCollection 2025 Apr. Arthroplast Today. 2025. PMID: 40115843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brunner L.C., Eshilian-Oates L., Kuo T.Y. Hip fractures in adults. Am. Fam. Physician. 2003;67:537–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources