Medicines for Obesity: Appraisal of Clinical Studies with Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation Tool
- PMID: 36771314
- PMCID: PMC9919203
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15030606
Medicines for Obesity: Appraisal of Clinical Studies with Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation Tool
Abstract
We evaluated the quality of evidence from phase III/IV clinical trials of drugs against obesity using the principles of Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) tool. Our systematic review evaluates the quality of clinical evidence from existing clinical trials and not the pharmacological efficacy of anti-obesity therapies. A literature search using select keywords in separate was performed in PubMed and ClinicalTrials.gov databases for phase III/IV clinical trials during the last ten years. Our findings indicate that the quality of existing clinical evidence from anti-obesity trials generally ranges from low to moderate. Most trials suffered from publication bias. Less frequently, trials suffered from the risk of bias mainly due to lack of blindness in the treatment. Our work indicates that additional higher-quality clinical trials are needed to gain more confidence in the estimate of the effect of currently used anti-obesity medicines, to allow more informed clinical decisions, thus reducing the risk of implementing potentially ineffective or even harmful therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: GRADE evaluation; clinical evidence; clinical pharmacology; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Theodosios D. Filippatos reports lecture honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, Mylan, Vi-atris, Astra Zeneca, Lilly, Recordati, Bausch Health, Servier and Innovis. All other authors report no conflicting interests.
Figures
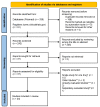
References
-
- Webster J.D., Hesp R., Garrow J.S. The Composition of Excess Weight in Obese Women Estimated by Body Density, Total Body Water and Total Body Potassium. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 1984;38:299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

