Insufficient Evidence of a Breastmilk Microbiota at Six-Weeks Postpartum: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 36771402
- PMCID: PMC9919471
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15030696
Insufficient Evidence of a Breastmilk Microbiota at Six-Weeks Postpartum: A Pilot Study
Abstract
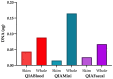
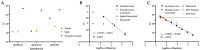
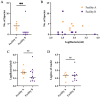
Breastmilk is thought to influence the infant gut by supplying prebiotics in the form of human milk oligosaccharides and potentially seeding the gut with breastmilk microbes. However, the presence of a breastmilk microbiota and origins of these microbes are still debated. As a pilot study, we assessed the microbes present in expressed breastmilk at six-weeks postpartum using shotgun metagenomic sequencing in a heterogenous cohort of women who delivered by vaginal (n = 8) and caesarean delivery (n = 8). In addition, we estimated the microbial load of breastmilk at six-weeks post-partum with quantitative PCR targeting the 16S rRNA gene. Breastmilk at six-weeks postpartum had a low microbial mass, comparable with PCR no-template and extraction controls. Microbes identified through metagenomic sequencing were largely consistent with skin and oral microbes, with four samples returning no identifiable bacterial sequences. Our results do not provide convincing evidence for the existence of a breastmilk microbiota at six-weeks postpartum. It is more likely that microbes present in breastmilk are sourced by ejection from the infant's mouth and from surrounding skin, as well as contamination during sampling and processing.
Keywords: breastmilk; contamination; infant; microbiome; retrograde inoculation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- The World Health Organisation Breastfeeding. 2021. [(accessed on 16 February 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/breastfeeding.
-
- Azad M.B., Konya T., Maughan H., Guttman D.S., Field C.J., Chari R.S., Sears M.R., Becker A.B., Scott J.A., Kozyrskyj A.L. Gut microbiota of healthy Canadian infants: Profiles by mode of delivery and infant diet at 4 months. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2013;185:385–394. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.121189. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stewart C.J., Ajami N.J., O’Brien J.L., Hutchinson D.S., Smith D.P., Wong M.C., Ross M.C., Lloyd R.E., Doddapaneni H., Metcalf G.A., et al. Temporal development of the gut microbiome in early childhood from the TEDDY study. Nature. 2018;562:583–588. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0617-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uzan-Yulzari A., Turta O., Belogolovski A., Ziv O., Kunz C., Perschbacher S., Neuman H., Pasolli E., Oz A., Ben-Amram H., et al. Neonatal antibiotic exposure impairs child growth during the first six years of life by perturbing intestinal microbial colonization. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:443. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20495-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

