The Impact of Phytochemicals in Obesity-Related Metabolic Diseases: Focus on Ceramide Metabolism
- PMID: 36771408
- PMCID: PMC9920427
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15030703
The Impact of Phytochemicals in Obesity-Related Metabolic Diseases: Focus on Ceramide Metabolism
Abstract
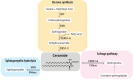
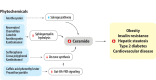
The prevalence of obesity and related metabolic diseases has increased dramatically worldwide. As obesity progresses, various lipid species accumulate in ectopic tissues. Amongst them, ceramides-a deleterious sphingolipid species-accumulate and cause lipotoxicity and metabolic disturbances. Dysregulated ceramide metabolism appears to be a key feature in the pathogenesis of obesity-related metabolic diseases. Notably, dietary modification might have an impact on modulating ceramide metabolism. Phytochemicals are plant-derived compounds with various physiological properties, which have been shown to protect against obesity-related metabolic diseases. In this review, we aim to examine the impact of a myriad of phytochemicals and their dietary sources in altering ceramide deposition and ceramide-related metabolism from in vitro, in vivo, and human clinical/epidemiological studies. This review discusses how numerous phytochemicals are able to alleviate ceramide-induced metabolic defects and reduce the risk of obesity-related metabolic diseases via diverse mechanisms.
Keywords: ceramide; metabolic disease; obesity; phytochemical; sphingolipid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ceramides - Lipotoxic Inducers of Metabolic Disorders.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Oct;26(10):538-550. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.07.006. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26412155 Review.
-
A ceramide-centric view of insulin resistance.Cell Metab. 2012 May 2;15(5):585-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.002. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22560211
-
Contribution of specific ceramides to obesity-associated metabolic diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 5;79(8):395. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04401-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35789435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Lard Works in Mysterious Ways: Ceramides in Nutrition-Linked Chronic Disease.Annu Rev Nutr. 2022 Aug 22;42:115-144. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-062220-112920. Epub 2022 May 18. Annu Rev Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35584813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramides in Metabolism: Key Lipotoxic Players.Annu Rev Physiol. 2021 Feb 10;83:303-330. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-093815. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Annu Rev Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33158378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spinal cord injury-induced metabolic impairment and steatohepatitis develops in non-obese rats and is exacerbated by premorbid obesity.Exp Neurol. 2024 Sep;379:114847. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114847. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38852834 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Interventions in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome.Nutrients. 2023 May 29;15(11):2513. doi: 10.3390/nu15112513. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299475 Free PMC article.
-
Echinacoside Induces UCP1- and ATP-Dependent Thermogenesis in Beige Adipocytes via the Activation of Dopaminergic Receptors.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 28;33(10):1268-1280. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2306.06041. Epub 2023 Jul 17. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37463854 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of a polyphenol-rich supplement on epigenetic and cellular markers of immune age: a pilot clinical study.Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 18;11:1474597. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1474597. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39628466 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Callistemon citrinus Leaf Phytosomes Against Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Rats Fed with a High-Fat-Fructose Diet.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 18;13(10):1263. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101263. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet. 2017;390:2627–2642. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32129-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keramat S.A., Alam K., Rana R.H., Chowdhury R., Farjana F., Hashmi R., Gow J., Biddle S.J.H. Obesity and the risk of developing chronic diseases in middle-aged and older adults: Findings from an Australian longitudinal population survey, 2009–2017. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0260158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260158. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

