The Efficacy of Panax ginseng for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies
- PMID: 36771427
- PMCID: PMC9919883
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15030721
The Efficacy of Panax ginseng for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies
Abstract
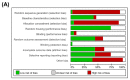
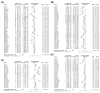
Although tremendous research has reported the protective effects of natural compounds in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), there is still no approved drug. This study aimed to examine the efficacy of Panax ginseng in NAFLD in preclinical studies. A total of 41 studies were identified by searching the PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases. The methodological quality was assessed by the risk of bias tool from the Systematic Review Center for Laboratory Animal Experimentation. The standardized mean difference (SMD) with a 95% confidence interval was calculated, and the random effects model was used to examine overall efficacy or heterogeneity. The publication bias was analyzed by Egger's test. The results showed that Panax ginseng treatment significantly reduced the systemic levels of alanine aminotransferase (SMD: -2.15 IU/L; p < 0.0001), aspartate aminotransferase (SMD: -2.86 IU/L; p < 0.0001), triglyceride (SMD: -2.86 mg/dL; p < 0.0001), total cholesterol (SMD: -1.69 mg/dL; p < 0.0001), low-density lipoprotein (SMD: -1.46 mg/dL; p < 0.0001), and fasting glucose (SMD: -1.45 mg/dL; p < 0.0001) while increasing high-density lipoprotein (SMD: 1.22 mg/dL; p = 0.0002) in NAFLD regardless of animal models or species. These findings may suggest that Panax ginseng is a promising therapeutic agent for NAFLD treatment.
Keywords: Panax ginseng; dyslipidemia; glucose tolerance; liver injury; meta-analysis; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Stockwell S., Trott M., Tully M., Shin J., Barnett Y., Butler L., McDermott D., Schuch F., Smith L. Changes in physical activity and sedentary behaviours from before to during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: A systematic review. BMJ. Open. Sport. Exerc. Med. 2021;7:e000960. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000960. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

