Medicinal Plants and Plant-Based Remedies in Grande-Terre: An Ethnopharmacological Approach
- PMID: 36771738
- PMCID: PMC9919082
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12030654
Medicinal Plants and Plant-Based Remedies in Grande-Terre: An Ethnopharmacological Approach
Abstract
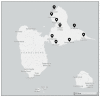
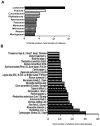
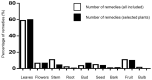
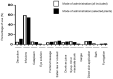
The island of Grande-Terre is a French overseas region that belongs to the Guadeloupean archipelago, a biodiversity hotspot with unique flora. Herbal medicine is widely used in the island for therapeutical purposes; however, there is a significant knowledge gap in the records relating to medicinal plants and their associated uses. Ethnobotanical survey methodology using quantitative parameters (informant consensus factor, species use value, relative frequency of citation, frequency use of a treatment and plant for an ailment) provided insights into the traditional medicinal use of a given plant. Ninety-six different plant species distributed among 56 families were identified and 523 remedies were documented in the survey. After data filtering, 22 plants species were associated with 182 remedies. The most frequent plant families were Poaceae, Myrtaceae, Cucurbitaceae and Rubiaceae. Aerial parts of these plants were the most common parts of the plant used for the remedies and the most frequent mode of administration was oral ingestion. This study highlights a valuable traditional knowledge of folklore medicine and helps to document and preserve the association of a plant with-and its use frequency for-a given ailment. These findings might be the starting point for the identification of biologically active phytocompounds to fight common health debilities.
Keywords: biology of medicinal plants; ethnobotany; ethnopharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- WHO . The WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy 2014–2023. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014.
-
- Barnes P.M., Bloom B., Nahin R.L. Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007. Nat. Health Stat. Rep. 2008;2007:1–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

