Advances in the Design of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Glucose-Sensitive Hydrogels
- PMID: 36771883
- PMCID: PMC9919422
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15030582
Advances in the Design of Phenylboronic Acid-Based Glucose-Sensitive Hydrogels
Abstract
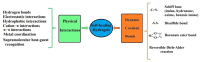
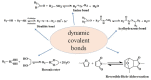
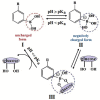
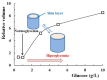
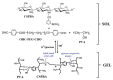
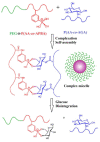
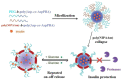
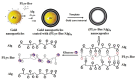
Diabetes, characterized by an uncontrolled blood glucose level, is the main cause of blindness, heart attack, stroke, and lower limb amputation. Glucose-sensitive hydrogels able to release hypoglycemic drugs (such as insulin) as a response to the increase of the glucose level are of interest for researchers, considering the large number of diabetes patients in the world (537 million in 2021, reported by the International Diabetes Federation). Considering the current growth, it is estimated that, up to 2045, the number of people with diabetes will increase to 783 million. The present work reviews the recent developments on the hydrogels based on phenylboronic acid and its derivatives, with sensitivity to glucose, which can be suitable candidates for the design of insulin delivery systems. After a brief presentation of the dynamic covalent bonds, the design of glucose-responsive hydrogels, the mechanism by which the hypoglycemic drug release is achieved, and their self-healing capacity are presented and discussed. Finally, the conclusions and the main aspects that should be addressed in future research are shown.
Keywords: dynamic covalent chemistry; glucose sensitivity; hydrogel; insulin releasing; phenylboronic acid; self-healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diboronate crosslinking: Introducing glucose specificity in glucose-responsive dynamic-covalent networks.J Control Release. 2022 Aug;348:601-611. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.016. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 35714732
-
A self-healing smart photonic crystal hydrogel sensor for glucose and related saccharides.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 May 28;188(6):210. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04849-3. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34047843
-
Recent Advances in Phenylboronic Acid-Based Gels with Potential for Self-Regulated Drug Delivery.Molecules. 2019 Mar 19;24(6):1089. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061089. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30893913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems: novel hydrogels and future applications.Regen Biomater. 2022 Aug 23;9:rbac056. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbac056. eCollection 2022. Regen Biomater. 2022. PMID: 36072265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucose-Responsive Injectable Thermogels via Dynamic-Covalent Cross-Linking of Pluronic Micelles.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022 Nov 14;8(11):4873-4885. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00979. Epub 2022 Nov 1. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022. PMID: 36317822
Cited by
-
Application of stimuli-responsive hydrogel in brain disease treatment.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 18;12:1450267. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1450267. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39091971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels for Protein Delivery.Gels. 2023 Oct 6;9(10):802. doi: 10.3390/gels9100802. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37888375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroresponsive Thiol-Yne Click-Hydrogels for Insulin Smart Delivery: Tackling Sustained Release and Leakage Control.ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2024 Jul 11;6(14):8093-8104. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.4c00911. eCollection 2024 Jul 26. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2024. PMID: 39839886 Free PMC article.
-
Cellulose-Based Hybrid Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Sustainable Approach.Gels. 2025 Jun 6;11(6):438. doi: 10.3390/gels11060438. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40558737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Insights into Glucose-Responsive Concanavalin A-Based Smart Hydrogels for Controlled Insulin Delivery.Gels. 2024 Apr 11;10(4):260. doi: 10.3390/gels10040260. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667679 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roy Biswas G., Mishra S., Sufian A. Gel Based Formulations in Oral Controlled Release Drug Delivery. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022;15:2357–2363. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00392. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

