Biosorbent Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Tricarboxi-Cellulose Designed to Retain Organic Dyes from Aqueous Media
- PMID: 36772016
- PMCID: PMC9919323
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15030715
Biosorbent Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Tricarboxi-Cellulose Designed to Retain Organic Dyes from Aqueous Media
Abstract
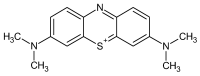
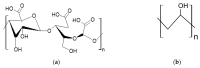
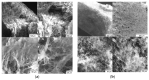
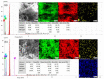
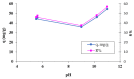
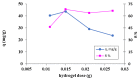
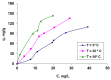
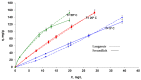
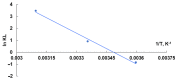
Methylene Blue, a cationic dye, was retained from aqueous solutions using a novel biosorbent made of poly(vinyl alcohol) reticulated with tricarboxi-cellulose produced via TEMPO oxidation (OxC25). The study of the Methylene Blue biosorption process was performed with an emphasis on operational parameters that may have an impact on it (such as biosorbent concentration, pH of the aqueous media, and temperature). The current study focused on three areas: (i) the physic-chemical characterization of the biosorbent (scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX)); (ii) biosorption data modeling to determine the quantitative characteristic parameters employing three equilibrium isotherms (Langmuir, Freundlich, and Dubinin-Radushkevich-DR); and (iii) the study of temperature influence. The results of the study showed that the Langmuir model provided a good fit for the experimental data of biosorption, realizing a maximum capacity of 806.45 mg/g at 20 °C. The free energy of biosorption (E) evaluated by the DR equation was in the range of 6.48-10.86 KJ/mol. The values of the thermodynamic parameters indicated an endothermic process because the free Gibbs energy ranged from -9.286 KJ/mol to -2.208 KJ/mol and the enthalpy was approximately -71.686 KJ/mol. The results obtained encourage and motivate the further study of this biosorption process by focusing on its kinetic aspects, establishing the biosorption's controlled steps, identifying the mechanism responsible for the retention of textile dyes presented in moderate concentration in aqueous media, and studying the biosorption process in a dynamic regime with a view to applying it to real systems.
Keywords: aqueous medium; biosorption; cationic organic dye; cellulose; hydrogel as biosorbent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrogel Based on Tricarboxi-Cellulose and Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Used as Biosorbent for Cobalt Ions Retention.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;13(9):1444. doi: 10.3390/polym13091444. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33947051 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides Used in Biosorbents Preparation for Organic Dyes Retaining from Aqueous Media.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;14(3):588. doi: 10.3390/polym14030588. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35160577 Free PMC article.
-
Biosorbents Based on Biopolymers from Natural Sources and Food Waste to Retain the Methylene Blue Dye from the Aqueous Medium.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 3;14(13):2728. doi: 10.3390/polym14132728. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808773 Free PMC article.
-
Marine alga "Bifurcaria bifurcata": biosorption of Reactive Blue 19 and methylene blue from aqueous solutions.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Sep;27(27):33636-33648. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07846-w. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32030583 Review.
-
A State-of-the-Art Review on Biowaste Derived Chitosan Biomaterials for Biosorption of Organic Dyes: Parameter Studies, Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamics.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 6;13(17):3009. doi: 10.3390/polym13173009. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Captivating actions of pomological crops waste as biosorbents for environmental remediation: a comprehensive review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Feb 14. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32156-w. Online ahead of print. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38351357 Review.
-
Adsorption of Acid Yellow 36 and direct blue 86 dyes to Delonix regia biochar-sulphur.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 27;15(1):3448. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85405-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39870714 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation of TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Hydrogels Modified with β-Cyclodextrin and κ-Carrageenan for Potential Adsorption Applications.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 28;10(1):972-984. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08188. eCollection 2025 Jan 14. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39829506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elgarahy A.M., Elwakeel K.Z., Mohammad S.H., Elshoubaky G.A. A critical review of biosorption of dyes, heavy metals and metalloids from wastewater as an efficient and green process. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021;4:100209. doi: 10.1016/j.clet.2021.100209. - DOI
-
- Nasrollahi Z., Hashemi M.-S., Bameri S., Taghvaee V.M. Environmental pollution, economic growth, population, industrialization, and technology in weak and strong sustainability: Using STIRPAT model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020;22:1105–1122. doi: 10.1007/s10668-018-0237-5. - DOI
-
- Cherniwchan J. Economic growth, industrialization, and the environment. Resour. Energy Econ. 2012;34:442–467. doi: 10.1016/j.reseneeco.2012.04.004. - DOI
-
- Hanafi M.F., Sapawe N. A review on the water problem associate with organic pollutants derived from phenol, methyl orange, and remazol brilliant blue dyes. Mater. Today Proc. 2020;31:A141–A150. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.258. - DOI
-
- Sirajudheen P., Poovathumkuzhi N.C., Vigneshwaran S., Chelaveettil B.M., Meenakshi S. Applications of chitin and chitosan based biomaterials for the adsorptive removal of textile dyes from water—A comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021;273:118604. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118604. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

