GRU-SVM Based Threat Detection in Cognitive Radio Network
- PMID: 36772366
- PMCID: PMC9921490
- DOI: 10.3390/s23031326
GRU-SVM Based Threat Detection in Cognitive Radio Network
Abstract
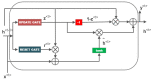
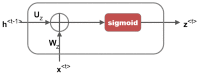
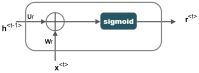
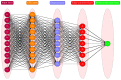
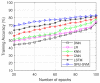
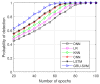
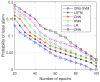
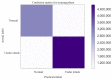
Cognitive radio networks are vulnerable to numerous threats during spectrum sensing. Different approaches can be used to lessen these attacks as the malicious users degrade the performance of the network. The cutting-edge technologies of machine learning and deep learning step into cognitive radio networks (CRN) to detect network problems. Several studies have been conducted utilising various deep learning and machine learning methods. However, only a small number of analyses have used gated recurrent units (GRU), and that too in software defined networks, but these are seldom used in CRN. In this paper, we used GRU in CRN to train and test the dataset of spectrum sensing results. One of the deep learning models with less complexity and more effectiveness for small datasets is GRU, the lightest variant of the LSTM. The support vector machine (SVM) classifier is employed in this study's output layer to distinguish between authorised users and malicious users in cognitive radio network. The novelty of this paper is the application of combined models of GRU and SVM in cognitive radio networks. A high testing accuracy of 82.45%, training accuracy of 80.99% and detection probability of 1 is achieved at 65 epochs in this proposed work.
Keywords: cognitive radio network; gated recurrent unit; malicious users; spectrum sensing; support vector machine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wang J., Liu H., Liu F. Research on deep learning method of intrusion attack prediction in software defined network; Proceedings of the ITM Web of Conferences; Tamil Nadu, India. 28–29 October 2022; p. 02042.
-
- Tang T.A., McLernon D., Mhamdi L., Zaidi S.A.R., Ghogho M. Deep Learning Applications for Cyber Security. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2019. Intrusion detection in sdn-based networks: Deep recurrent neural network approach; pp. 175–195.
-
- Wu Y., Wei D., Feng J. Network attacks detection methods based on deep learning techniques: A survey. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2020;2020:8872923. doi: 10.1155/2020/8872923. - DOI
-
- Bastola S.B., Shakya S., Sharma S. Distributed Denial of Service Attack Detection on Software Defined Networking Using Deep Learning; Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI); Udupi, India. 13–16 September 2021.
-
- Parvin S., Hussain F.K., Hussain O.K., Han S., Tian B., Chang E. Cognitive radio network security: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2012;35:1691–1708. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2012.06.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

