Swarm Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: A Review
- PMID: 36772503
- PMCID: PMC9920579
- DOI: 10.3390/s23031466
Swarm Intelligence in Internet of Medical Things: A Review
Abstract
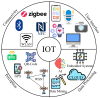
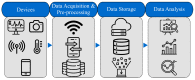
Continuous advancements of technologies such as machine-to-machine interactions and big data analysis have led to the internet of things (IoT) making information sharing and smart decision-making possible using everyday devices. On the other hand, swarm intelligence (SI) algorithms seek to establish constructive interaction among agents regardless of their intelligence level. In SI algorithms, multiple individuals run simultaneously and possibly in a cooperative manner to address complex nonlinear problems. In this paper, the application of SI algorithms in IoT is investigated with a special focus on the internet of medical things (IoMT). The role of wearable devices in IoMT is briefly reviewed. Existing works on applications of SI in addressing IoMT problems are discussed. Possible problems include disease prediction, data encryption, missing values prediction, resource allocation, network routing, and hardware failure management. Finally, research perspectives and future trends are outlined.
Keywords: internet of medical things; internet of things; internet of things in health; swarm intelligence algorithm; wearable devices; wireless sensor network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Survey of Using Swarm Intelligence Algorithms in IoT.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Mar 5;20(5):1420. doi: 10.3390/s20051420. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32150912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Assisted Biomedical Systems for Intelligent Healthcare.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 25;12(8):562. doi: 10.3390/bios12080562. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Wireless Sensor Networks and Internet of Things Technologies-Foundations of Smart Healthcare.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jun 27;20(13):3619. doi: 10.3390/s20133619. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32605071 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Healthcare through Sensor-Enabled Digital Twins in Smart Environments: A Comprehensive Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;24(9):2793. doi: 10.3390/s24092793. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38732899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secure Smart Wearable Computing through Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems for Health Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;22(3):1076. doi: 10.3390/s22031076. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35161820 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An Improved Harris Hawks Optimization Algorithm and Its Application in Grid Map Path Planning.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;8(5):428. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8050428. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754179 Free PMC article.
-
Body composition predicts hypertension using machine learning methods: a cohort study.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 27;13(1):6885. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34127-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37105977 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-Inspired Internet of Things: Current Status, Benefits, Challenges, and Future Directions.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Aug 17;8(4):373. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8040373. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37622978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Adaptive Intrusion Detection System in the Internet of Medical Things Using Fuzzy-Based Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 17;23(22):9247. doi: 10.3390/s23229247. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005635 Free PMC article.
-
An Improved Mutual Information Feature Selection Technique for Intrusion Detection Systems in the Internet of Medical Things.Sensors (Basel). 2023 May 22;23(10):4971. doi: 10.3390/s23104971. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37430886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gubbi J., Buyya R., Marusic S., Palaniswami M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2013;29:1645–1660. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2013.01.010. - DOI
-
- Sotomayor M., Pérez-Castrillo J.D., Castiglione F. Complex Social and Behavioral Systems: Game Theory and Agent-Based Models. Springer Nature; Berlin, Germany: 2020.
-
- Fister Jr I., Yang X.S., Fister I., Brest J., Fister D. A brief review of nature-inspired algorithms for optimization. arXiv. 20131307.4186
-
- Boveiri H.R., Khayami R., Elhoseny M., Gunasekaran M. An efficient Swarm-Intelligence approach for task scheduling in cloud-based internet of things applications. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019;10:3469–3479. doi: 10.1007/s12652-018-1071-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

