Person Re-Identification with RGB-D and RGB-IR Sensors: A Comprehensive Survey
- PMID: 36772548
- PMCID: PMC9919319
- DOI: 10.3390/s23031504
Person Re-Identification with RGB-D and RGB-IR Sensors: A Comprehensive Survey
Abstract
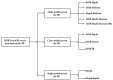
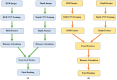
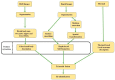
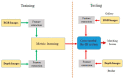
Learning about appearance embedding is of great importance for a variety of different computer-vision applications, which has prompted a surge in person re-identification (Re-ID) papers. The aim of these papers has been to identify an individual over a set of non-overlapping cameras. Despite recent advances in RGB-RGB Re-ID approaches with deep-learning architectures, the approach fails to consistently work well when there are low resolutions in dark conditions. The introduction of different sensors (i.e., RGB-D and infrared (IR)) enables the capture of appearances even in dark conditions. Recently, a lot of research has been dedicated to addressing the issue of finding appearance embedding in dark conditions using different advanced camera sensors. In this paper, we give a comprehensive overview of existing Re-ID approaches that utilize the additional information from different sensor-based methods to address the constraints faced by RGB camera-based person Re-ID systems. Although there are a number of survey papers that consider either the RGB-RGB or Visible-IR scenarios, there are none that consider both RGB-D and RGB-IR. In this paper, we present a detailed taxonomy of the existing approaches along with the existing RGB-D and RGB-IR person Re-ID datasets. Then, we summarize the performance of state-of-the-art methods on several representative RGB-D and RGB-IR datasets. Finally, future directions and current issues are considered for improving the different sensor-based person Re-ID systems.
Keywords: RGB–D sensors; RGB–IR sensors; cross-modal; multi-modal; re-identification; video surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












References
-
- Gheissari N., Sebastian T.B., Hartley R. Person reidentification using spatiotemporal appearance; Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and pattern Recognition; New York, NY, USA. 17–22 June 2006; pp. 1528–1535.
-
- Islam K. Person search: New paradigm of person re-identification: A survey and outlook of recent works. Image Vis. Comput. 2020;101:103970. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2020.103970. - DOI
-
- Zheng L., Yang Y., Hauptmann A.G. Person re-identification: Past, Present and Future. arXiv. 20161610.02984
-
- Wu D., Zheng S.J., Zhang X.P., Yuan C.A., Cheng F., Zhao Y., Lin Y.J., Zhao Z.Q., Jiang Y.L., Huang D.S. Deep learning-based methods for person re-identification: A comprehensive review. Neurocomputing. 2019;337:354–371. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.01.079. - DOI
-
- Bedagkar-Gala A., Shah S.K. A survey of approaches and trends in person re-identification. Image Vis. Comput. 2014;32:270–286. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2014.02.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

