Computer-Aided Ankle Ligament Injury Diagnosis from Magnetic Resonance Images Using Machine Learning Techniques
- PMID: 36772604
- PMCID: PMC9919370
- DOI: 10.3390/s23031565
Computer-Aided Ankle Ligament Injury Diagnosis from Magnetic Resonance Images Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract
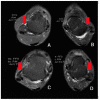
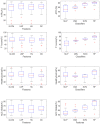
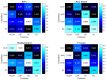
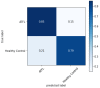
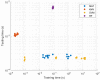
Ankle injuries caused by the Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) are the most common type of injury. Thus, finding new ways to analyze these injuries through novel technologies is critical for assisting medical diagnosis and, as a result, reducing the subjectivity of this process. As a result, the purpose of this study is to compare the ability of specialists to diagnose lateral tibial tuberosity advancement (LTTA) injury using computer vision analysis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The experiments were carried out on a database obtained from the Vue PACS-Carestream software, which contained 132 images of ATFL and normal (healthy) ankles. Because there were only a few images, image augmentation techniques was used to increase the number of images in the database. Following that, various feature extraction algorithms (GLCM, LBP, and HU invariant moments) and classifiers such as Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), Support Vector Machine (SVM), k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN), and Random Forest (RF) were used. Based on the results from this analysis, for cases that lack clear morphologies, the method delivers a hit rate of 85.03% with an increase of 22% over the human expert-based analysis.
Keywords: MRI; ankle ligament injury; data augmentation; feature extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intelligent localization and quantitative evaluation of anterior talofibular ligament injury using magnetic resonance imaging of ankle.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Aug 28;21(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00660-x. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34454471 Free PMC article.
-
T2 -Mapping evaluation of early cartilage alteration of talus for chronic lateral ankle instability with isolated anterior talofibular ligament tear or combined with calcaneofibular ligament tear.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 Jan;47(1):69-77. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25745. Epub 2017 Apr 27. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 28449249
-
3D MRI evaluation of morphological characteristics of lateral ankle ligaments in injured patients and uninjured controls.J Orthop Sci. 2020 Jan;25(1):183-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2019.02.018. Epub 2019 Mar 16. J Orthop Sci. 2020. PMID: 30885728
-
Imaging diagnosis for anterior talofibular ligament injury: a systemic review with meta-analysis.Acta Radiol. 2023 Feb;64(2):612-624. doi: 10.1177/02841851221080556. Epub 2022 Mar 27. Acta Radiol. 2023. PMID: 35343253
-
Ankle ultrasound for detecting anterior talofibular ligament tear using operative finding as reference standard: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020 Feb;46(1):73-81. doi: 10.1007/s00068-019-01169-3. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020. PMID: 31187159
Cited by
-
Development and validation of radiomics model for MRI-based identification of anterior talofibular ligament injuries.Sci Rep. 2025 May 4;15(1):15575. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99813-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40320488 Free PMC article.
-
Automated radiography assessment of ankle joint instability using deep learning.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 29;15(1):15012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99620-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40301608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Renström A.F.H. and Scott A. Lynch Ankle ligament injuries. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte. 1998;4:71–80. doi: 10.1590/S1517-86921998000300002. - DOI
-
- Tao H., Hu Y., Qiao Y., Ma K., Yan X., Hua Y., Chen S. T2-mapping evaluation of early cartilage alteration of talus for chronic lateral ankle instability with isolated anterior talofibular ligament tear or combined with calcaneofibular ligament tear. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2018;47:69–77. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25745. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

