At the Confluence of Artificial Intelligence and Edge Computing in IoT-Based Applications: A Review and New Perspectives
- PMID: 36772680
- PMCID: PMC9920982
- DOI: 10.3390/s23031639
At the Confluence of Artificial Intelligence and Edge Computing in IoT-Based Applications: A Review and New Perspectives
Abstract
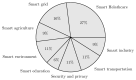
Given its advantages in low latency, fast response, context-aware services, mobility, and privacy preservation, edge computing has emerged as the key support for intelligent applications and 5G/6G Internet of things (IoT) networks. This technology extends the cloud by providing intermediate services at the edge of the network and improving the quality of service for latency-sensitive applications. Many AI-based solutions with machine learning, deep learning, and swarm intelligence have exhibited the high potential to perform intelligent cognitive sensing, intelligent network management, big data analytics, and security enhancement for edge-based smart applications. Despite its many benefits, there are still concerns about the required capabilities of intelligent edge computing to deal with the computational complexity of machine learning techniques for big IoT data analytics. Resource constraints of edge computing, distributed computing, efficient orchestration, and synchronization of resources are all factors that require attention for quality of service improvement and cost-effective development of edge-based smart applications. In this context, this paper aims to explore the confluence of AI and edge in many application domains in order to leverage the potential of the existing research around these factors and identify new perspectives. The confluence of edge computing and AI improves the quality of user experience in emergency situations, such as in the Internet of vehicles, where critical inaccuracies or delays can lead to damage and accidents. These are the same factors that most studies have used to evaluate the success of an edge-based application. In this review, we first provide an in-depth analysis of the state of the art of AI in edge-based applications with a focus on eight application areas: smart agriculture, smart environment, smart grid, smart healthcare, smart industry, smart education, smart transportation, and security and privacy. Then, we present a qualitative comparison that emphasizes the main objective of the confluence, the roles and the use of artificial intelligence at the network edge, and the key enabling technologies for edge analytics. Then, open challenges, future research directions, and perspectives are identified and discussed. Finally, some conclusions are drawn.
Keywords: Internet of things; artificial intelligence; big data analytics; bioinspired metaheuristic algorithms; deep learning; edge analytics; edge computing; machine learning; resource management; swarm intelligence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AI augmented edge and fog computing for Internet of Health Things (IoHT).PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025 Jan 30;11:e2431. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2431. eCollection 2025. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025. PMID: 40062251 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid computing framework security in dynamic offloading for IoT-enabled smart home system.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Aug 23;10:e2211. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2211. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39314732 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Applications and Self-Learning 6G Networks for Smart Cities Digital Ecosystems: Taxonomy, Challenges, and Future Directions.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 1;22(15):5750. doi: 10.3390/s22155750. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35957307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A service-oriented microservice framework for differential privacy-based protection in industrial IoT smart applications.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 9;15(1):29230. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15077-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40783426 Free PMC article.
-
Internet of Things in Space: A Review of Opportunities and Challenges from Satellite-Aided Computing to Digitally-Enhanced Space Living.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 4;21(23):8117. doi: 10.3390/s21238117. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34884122 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring technology acceptance of flight simulation training devices and augmented reality in general aviation pilot training.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 17;15(1):2302. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85448-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39824908 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Internet of Things Systems: A Systematic Mapping Study.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Oct 10;24(20):6511. doi: 10.3390/s24206511. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual smart sensor data-based deep learning network for premature infant hypoglycemia detection.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23442. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03864-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603339 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Performance and Power Optimization with Heterogeneous Processing-in-Memory for AI Applications on Edge Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;15(10):1222. doi: 10.3390/mi15101222. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459096 Free PMC article.
-
Fog-based deep learning framework for real-time pandemic screening in smart cities from multi-site tomographies.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 May 27;24(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01302-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38797827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohammadi M., Al-Fuqaha A., Sorour S., Guizani M. Deep Learning for IoT Big Data and Streaming Analytics: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018;20:2923–2960. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2844341. - DOI
-
- Zhou Z., Chen X., Li E., Zeng L., Luo K., Zhang J. Edge Intelligence: Paving the Last Mile of Artificial Intelligence with Edge Computing. Proc. IEEE. 2019;107:1738–1762. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2918951. - DOI
-
- Chang Z., Liu S., Xiong X., Cai Z., Tu G. A Survey of Recent Advances in Edge-Computing-Powered Artificial Intelligence of Things. IEEE IoT J. 2021;8:13849–13875. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3088875. - DOI
-
- Osifeko M.O., Hancke G.P. Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Cognitive Sensing in Future IoT: State-of-the-Art, Potentials, and Challenges. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2020;9:21. doi: 10.3390/jsan9020021. - DOI
-
- Zhang W., Wang J., Han G., Huang S., Feng Y., Shu L. A Data Set Accuracy Weighted Random Forest Algorithm for IoT Fault Detection Based on Edge Computing and Blockchain. IEEE IoT J. 2021;8:2354–2363. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3044934. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

