Core versus Surface Sensors for Reinforced Concrete Structures: A Comparison of Fiber-Optic Strain Sensing to Conventional Instrumentation
- PMID: 36772785
- PMCID: PMC9919918
- DOI: 10.3390/s23031745
Core versus Surface Sensors for Reinforced Concrete Structures: A Comparison of Fiber-Optic Strain Sensing to Conventional Instrumentation
Abstract
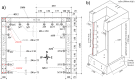
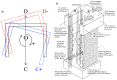
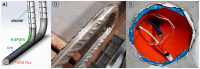
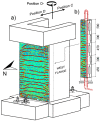
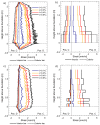
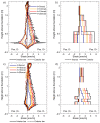
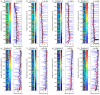
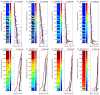
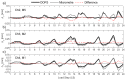
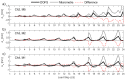
High-resolution distributed reinforcement strain measurements can provide invaluable information for developing and evaluating numerical and analytical models of reinforced concrete structures. A recent testing campaign conducted at UCLouvain in Belgium used fiber-optic sensors embedded along several longitudinal steel rebars of three reinforced concrete U-shaped walls. The resulting experimental dataset provides an opportunity to evaluate and compare, for different types of loading, the strain measurements obtained with the fiber-optic sensors in the confined core of the structural member against more conventional and state-of-the-practice sensors that monitor surface displacements and deformations. This work highlights the need to average strain measurements from digital image correlation techniques in order to obtain coherent results with the strains measured from fiber optics, and investigates proposals to achieve this relevant goal for research and engineering practices. The longitudinal strains measured by the fiber optics also provide additional detailed information on the behavior of these wall units compared to the more conventional instrumentation, such as strain penetration into the foundation and head of the wall units, which are studied in detail.
Keywords: DFOS; DIC; DOFS; RC; fiber optic; optical; strain penetration; walls; yield.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Distributed Fiber-Optic Strain Sensing of an Innovative Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column Connection.Sensors (Basel). 2022 May 23;22(10):3957. doi: 10.3390/s22103957. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35632369 Free PMC article.
-
Brillouin corrosion expansion sensors for steel reinforced concrete structures using a fiber optic coil winding method.Sensors (Basel). 2011;11(11):10798-819. doi: 10.3390/s111110798. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Sensors (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22346672 Free PMC article.
-
Embedded Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors in Reinforced Concrete Structures-A Case Study.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Mar 26;18(4):980. doi: 10.3390/s18040980. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29587449 Free PMC article.
-
Fiber Optic Sensors Embedded in Textile-Reinforced Concrete for Smart Structural Health Monitoring: A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 21;21(15):4948. doi: 10.3390/s21154948. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34372185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors for Civil Engineering Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2016 May 23;16(5):748. doi: 10.3390/s16050748. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27223289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Liquids and Saturated Salt Solutions on Polymer-Coated Fiber Optic Sensors for Distributed Strain and Temperature Measurement.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;24(14):4659. doi: 10.3390/s24144659. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39066056 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenges and Advantages of Distributed Fiber Optic Strain Monitoring in and on the Cementitious Matrix of Concrete Beams.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;23(23):9477. doi: 10.3390/s23239477. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scott R., Gill P.A. Short-term distributions of strain and bond stress along tension reinforcement. Struct. Eng. 1987;65:39–43.
-
- Kaklauskas G. Crack Model for RC Members Based on Compatibility of Stress-Transfer and Mean-Strain Approaches. J. Struct. Eng. 2017;143:04017105. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001842. - DOI
-
- Shima H., Chou L.-L., Okamura H. Micro and macro models for bond in reinforced concrete. J. Fac. Eng. 1987;39:133–194.
-
- Woods J.E., Lau D.T., Bao X., Li W. Measuring strain fields in FRP strengthened RC shear walls using a distributed fiber optic sensor. Eng. Struct. 2017;152:359–369. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.09.034. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

