Hydroxyapatite-coated compared with stainless steel external fixation pins did not show impact in the rate of pin track infection: a multicenter prospective study
- PMID: 36773051
- PMCID: PMC9918829
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-023-05717-w
Hydroxyapatite-coated compared with stainless steel external fixation pins did not show impact in the rate of pin track infection: a multicenter prospective study
Abstract
Purpose: Infection at the pin site remains the most common complication of external fixators (EFs). It is known that hydroxyapatite (HA)-coated pins increase bone adhesion and may lead to reduced rates of reported infections. The present study compares the rates of pin track infection associated with stainless steel and HA-coated pins.
Methods: This is a prospective, multicenter, nonrandomized, comparative intervention study among patients undergoing surgical treatment with EFs of any type between April 2018 and October 2021. Patients were followed up until the removal of the EF, or the end of the study period (ranging from 1 to 27.6 months). The definition of pin track infection was based upon the Maz-Oxford-Nuffield (MON) pin infection grading system.
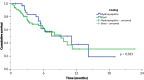
Results: Overall, 132 patients undergoing external fixation surgery were included. Of these, 94 (71.2%) were male, with a mean age of 36.9 years (SD ± 18.9). Infection of any type (score > 1) was observed in 63 (47.7%) patients. Coated and uncoated-pin track-infection occurred in 45.7% and 48.5% of patients, respectively (P= 0.0887). The probability of developing infection (defined as a score ≥ 2) adjusted for comorbidities and follow-up time was not statistically higher among those who received uncoated pins compared to those who received pins coated with HA (odds ratio (OR) = 1.56, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 0.67-3.67, p <0.05).
Conclusion: In the present study, the external fixator pin infection rates were similar when using HA coating and standard steel pins.
Keywords: Coated pin; External fixator; Hydroxyapatite; Pin insertion site infection; Stainless steel pin.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to SICOT aisbl.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydroxyapatite-coated Schanz pins in external fixators used for distraction osteogenesis : a randomized, controlled trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002 Jul;84(7):1162-6. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200207000-00011. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. PMID: 12107316 Clinical Trial.
-
Antimicrobial efficacy of external fixator pins coated with a lipid stabilized hydroxyapatite/chlorhexidine complex to prevent pin tract infection in a goat model.J Trauma. 2001 Jun;50(6):1008-14. doi: 10.1097/00005373-200106000-00006. J Trauma. 2001. PMID: 11426113
-
Role of coatings and materials of external fixation pins on the rates of pin tract infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Orthop. 2021 Nov 18;12(11):920-930. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i11.920. eCollection 2021 Nov 18. World J Orthop. 2021. PMID: 34888152 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxyapatite pins for external fixation: is there sufficient evidence to prove that coated pins are less likely to be replaced prematurely?Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(4):410-5. doi: 10.3944/AOTT.2015.14.0206. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015. PMID: 26312469 Review.
-
State of the art review: techniques to avoid pin loosening and infection in external fixation.J Orthop Trauma. 2002 Mar;16(3):189-95. doi: 10.1097/00005131-200203000-00009. J Orthop Trauma. 2002. PMID: 11880783 Review.
Cited by
-
[Comparative study of external fixator combined with Kirschner wire fixation and Kirschner wires fixation in treatment of cubitus varus deformity in children].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Mar 15;38(3):284-289. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202312045. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38500420 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
In-vitro external fixation pin-site model proof of concept: A novel approach to studying wound healing in transcutaneous implants.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2024 Apr;238(4):403-411. doi: 10.1177/09544119241234154. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2024. PMID: 38602217 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of Microbiological Findings on the Surface of External Fixator Pins Comparing Steel Pins with Hydroxyapatite-Coated Pins].Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2025 Jun 23;60(2):1-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0045-1809519. eCollection 2025 Apr. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 40552005 Free PMC article. Portuguese.
-
Analysis of Microbiological Findings on the Surface of External Fixator Pins Comparing Steel Pins with Hydroxyapatite-Coated Pins.Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2025 Jun 23;60(2):1-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0045-1809337. eCollection 2025 Apr. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 40551995 Free PMC article.
-
Pin-tract infection is an important factor associated with pin loosening during external fixation: a prospective analysis of 47 consecutive patients.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Mar 27;15:1459205. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1459205. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40212847 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous