Molecular and cellular basis of the dose-rate-dependent adverse effects of radiation exposure in animal models. Part I: Mammary gland and digestive tract
- PMID: 36773323
- PMCID: PMC10036108
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrad002
Molecular and cellular basis of the dose-rate-dependent adverse effects of radiation exposure in animal models. Part I: Mammary gland and digestive tract
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Molecular and cellular basis of the dose-rate-dependent adverse effects of radiation exposure in animal models. Part I: Mammary gland and digestive tract.J Radiat Res. 2023 May 25;64(3):633. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrad038. J Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 37105533 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
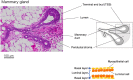
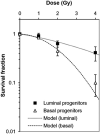
While epidemiological data are available for the dose and dose-rate effectiveness factor (DDREF) for human populations, animal models have contributed significantly to providing quantitative data with mechanistic insights. The aim of the current review is to compile both the in vitro experiments with reference to the dose-rate effects of DNA damage and repair, and the animal studies, specific to rodents, with reference to the dose-rate effects of cancer development. In particular, the review focuses especially on the results pertaining to underlying biological mechanisms and discusses their possible involvement in the process of radiation-induced carcinogenesis. Because the concept of adverse outcome pathway (AOP) together with the key events has been considered as a clue to estimate radiation risks at low doses and low dose-rates, the review scrutinized the dose-rate dependency of the key events related to carcinogenesis, which enables us to unify the underlying critical mechanisms to establish a connection between animal experimental studies with human epidemiological studies.
Keywords: animal; cancer; cell; epidemiology; low dose; low dose rate; radiation.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- UNSCEAR . Levels and effects of radiation exposure due to the nuclear accident after the 2011 great east-Japan earthquake and tsunami. UNSCEAR 2013 Report. Volume I, Scientific Annex a. New York: United Nations, 2013, 2014, 1–311.
-
- ICRP 2007 . The 2007 recommendations of ICRP. ICRP publication 103. Ann ICRP 2007;37:1–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

