Genomic and transcriptomic analyses identify a prognostic gene signature and predict response to therapy in pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma
- PMID: 36773602
- PMCID: PMC9975319
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100938
Genomic and transcriptomic analyses identify a prognostic gene signature and predict response to therapy in pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma
Abstract
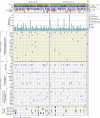
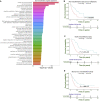
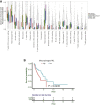
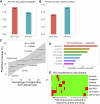
Malignant mesothelioma is an aggressive cancer with limited treatment options and poor prognosis. A better understanding of mesothelioma genomics and transcriptomics could advance therapies. Here, we present a mesothelioma cohort of 122 patients along with their germline and tumor whole-exome and tumor RNA sequencing data as well as phenotypic and drug response information. We identify a 48-gene prognostic signature that is highly predictive of mesothelioma patient survival, including CCNB1, the expression of which is highly predictive of patient survival on its own. In addition, we analyze the transcriptomics data to study the tumor immune microenvironment and identify synthetic-lethality-based signatures predictive of response to therapy. This germline and somatic whole-exome sequencing as well as transcriptomics data from the same patient are a valuable resource to address important biological questions, including prognostic biomarkers and determinants of treatment response in mesothelioma.
Keywords: WES; mesothelioma; response to therapy; synthetic lethality; transcriptome.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests E.R. is a co-founder of Medaware, Metabomed, and Pangea Biomed (divested from the latter). He serves as a non-paid scientific consultant to Pangea Biomed under a collaboration agreement between Pangea Biomed and the NCI. R.H. has received funding for conduct of clinical trials via a cooperative research and development agreement between NCI and Bayer AG and TCR2 Therapeutics. J.S.L. is a scientific consultant of Pangea Therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Vogelzang N.J., Rusthoven J.J., Symanowski J., Denham C., Kaukel E., Ruffie P., Gatzemeier U., Boyer M., Emri S., Manegold C., et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003;21:2636–2644. - PubMed
-
- Baas P., Scherpereel A., Nowak A.K., Fujimoto N., Peters S., Tsao A.S., Mansfield A.S., Popat S., Jahan T., Antonia S., et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:375–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

