Mast cells contribute to the resolution of allergic inflammation by releasing resolvin D1
- PMID: 36773709
- PMCID: PMC10285510
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106691
Mast cells contribute to the resolution of allergic inflammation by releasing resolvin D1
Abstract
Background: Mast cells are initiators and main effectors of allergic inflammation, together with eosinophils, with whom they can interact in a physical and soluble cross-talk with marked pro-inflammatory features, the Allergic Effector Unit. The pro-resolution role of mast cells, alone or in co-culture with eosinophils, has not been characterized yet.
Objectives: We aimed to investigate select pro-resolution pathways in mast cells in vitro and in vivo in allergic inflammation.
Methods: In vitro, we employed human and murine mast cells and analyzed release of resolvin D1 and expression of 15-lipoxygenase after IgE-mediated activation. We performed co-culture of IgE-activated mast cells with peripheral blood eosinophils and investigated 15-lipoxygenase expression and Resolvin D1 release. In vivo, we performed Ovalbumin/Alum and Ovalbumin/S. aureus enterotoxin B allergic peritonitis model in Wild Type mice following a MC "overshoot" protocol.
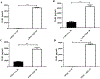
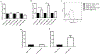
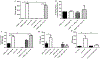
Results: We found that IgE-activated mast cells release significant amounts of resolvin D1 30 min after activation, while 15-lipoxygenase expression remained unchanged. Resolvin D1 release was found to be decreased in IgE-activated mast cells co-cultured with peripheral blood eosinophils for 30 min In vivo, mast cell-overshoot mice exhibited a trend of reduced inflammation, together with increased peritoneal resolvin D1 release.
Conclusions: Mast cells can actively contribute to resolution of allergic inflammation by releasing resolvin D1.
Keywords: Allergic inflammation; Allergic peritonitis; Eosinophils; Mast cells; Resolution; Resolvin D1.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests statement The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

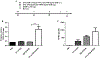

Similar articles
-
Cromolyn Sodium differentially regulates human mast cell and mouse leukocyte responses to control allergic inflammation.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Apr;178:106172. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106172. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 35278626
-
A novel mast cell-dependent allergic peritonitis model.Clin Exp Immunol. 2021 Sep;205(3):306-315. doi: 10.1111/cei.13619. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33999404 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of resolvin D1, a pro-resolving lipid mediator, in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small intestinal damage.PLoS One. 2021 May 4;16(5):e0250862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250862. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33945545 Free PMC article.
-
IgE, mast cells, and eosinophils in atopic dermatitis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Dec;41(3):298-310. doi: 10.1007/s12016-011-8252-4. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21249468 Review.
-
Effects of eosinophils on mast cells: a new pathway for the perpetuation of allergic inflammation.Mol Immunol. 2002 Sep;38(16-18):1369. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00090-1. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12217410 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid mediators in neutrophil biology: inflammation, resolution and beyond.Curr Opin Hematol. 2024 Jul 1;31(4):175-192. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000822. Epub 2024 May 7. Curr Opin Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38727155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Lipid Metabolism of Value in Cancer Research and Treatment? Part II: Role of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Inflammation, Infections, and Cancer.Metabolites. 2024 May 29;14(6):314. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060314. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38921449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proresolving Lipid Mediators in the Respiratory System.Annu Rev Physiol. 2025 Feb;87(1):491-512. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020924-033209. Epub 2025 Feb 3. Annu Rev Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39303274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Endogenous Specialized Proresolving Mediators in Mast Cells and Their Involvement in Inflammation and Resolution.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 11;26(4):1491. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041491. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003957 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elishmereni M, Alenius HT, Bradding P, Mizrahi S, Shikotra A, Minai-Fleminger Y, Mankuta D, Eliashar R, Zabucchi G, Levi-Schaffer F, Physical interactions between mast cells and eosinophils: a novel mechanism enhancing eosinophil survival in vitro., Allergy. 66 (2011) 376–85. 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02494.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

