Maternal nutritional status and milk volume and composition in India: an observational study
- PMID: 36773786
- PMCID: PMC10273082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.02.002
Maternal nutritional status and milk volume and composition in India: an observational study
Abstract
Background: Human milk provides essential nutrition for infants, and its benefits are well established. We lack data on the influence of maternal nutritional status on milk volume and composition in low-middle income countries.
Objective: We aimed to 1) assess lactation performance (human milk volume, macronutrient composition, and infant energy intake) in Indian females and 2) examine the associations between maternal anthropometry (BMI, percentage body fat) and lactation performance.
Methods: We conducted an observational study among 232 mother-infant dyads, 2 to 4 mo postpartum in Haryana, India. We used deuterium oxide dose-to-mother technique to measure milk volume and maternal percentage body fat and collected human milk samples to determine macronutrient and energy concentrations. Adjusted multiple linear regression models were used to examine the associations between maternal anthropometry and lactation performance.
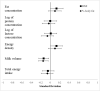
Results: The mean BMI and percentage body fat of mothers were 21.7 ± 3.6 kg/m2 and 29.5 ± 7.7, respectively. Milk volume and macronutrient composition were similar to the reference values (means ± standard deviations: milk volume, 724 ± 184 mL/d; median (25th, 75th percentile); protein, 9.9 (8.3, 11.7) g/L; fat, 41.0 ± 15.2 g/L; energy density, 0.71 ± 0.14 kcal/g; lactose, 65.5 (55.3, 71.3) g/L). Maternal BMI and percentage body fat were not significantly associated with macronutrient composition. Both maternal BMI and percentage body fat were negatively associated with milk volume (-7.0, 95% CI: -12.4, -1.6 mL/d; -3.5, 95% CI: -6.0, -1.1mL/d, respectively) but there were no effects on the total energy intake of infants after adjusting for covariates.
Conclusion: Most mothers had a normal BMI and milk of similar composition and volume to reference values. Future work in populations with a greater burden of underweight and/or obesity are needed to examine the underlying mechanisms between maternal body composition and milk volume. This trial was registered at The Clinical Trials Registry- India as CTRI/2017/01/007636.
Keywords: India; body composition; breastfeeding; human milk intake; infant intake; maternal nutrition.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- de Onis M., Onyango A.W., Borghi E., Garza C., Yang H. Comparison of the World Health Organization (WHO) child growth standards and the National Center for Health Statistics/WHO international growth reference: implications for child health programmes. Public. Health. Nutr. 2006;9:942–947. doi: 10.1017/phn20062005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) and I.C.F. IIPS; Mumbai: 2021. National Family Healthy Survey (NFHS-5), India, 2019-21: Haryana.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

