Nimesulide, a COX-2 inhibitor, sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by promoting DR5 clustering †
- PMID: 36775838
- PMCID: PMC9928464
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2023.2176692
Nimesulide, a COX-2 inhibitor, sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by promoting DR5 clustering †
Abstract
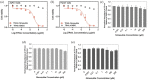
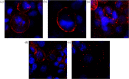
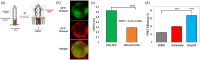
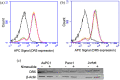
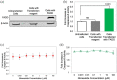
Nimesulide is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and a COX-2 inhibitor with antitumor and antiproliferative activities that induces apoptosis in oral, esophagus, breast, and pancreatic cancer cells. Despite being removed from the market due to hepatotoxicity, nimesulide is still an important research tool being used to develop new anticancer drugs. Multiple studies have been done to modify the nimesulide skeleton to develop more potent anticancer agents and related compounds are promising scaffolds for future development. As such, establishing a mechanism of action for nimesulide remains an important part of realizing its potential. Here, we show that nimesulide enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in resistant pancreatic cancer cells by promoting clustering of DR5 in the plasma membrane. In this way, nimesulide acts like a related compound, DuP-697, which sensitizes TRAIL-resistant colon cancer cells in a similar manner. Our approach applies a time-resolved FRET-based biosensor that monitors DR5 clustering and conformational states in the plasma membrane. We show that this tool can be used for future high-throughput screens to identify novel, nontoxic small molecule scaffolds to overcome TRAIL resistance in cancer cells.
Keywords: COX-2 inhibitors; Nimesulide; TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand; death receptor 5; pancreatic cancer cells; tumor necrosis factor receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
D.D.T. holds equity in and serves as executive officers for Photonic Pharma LLC, a company that owns intellectual property related to technology used in part of this project. These relationships have been reviewed and managed by the University of Minnesota in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Dai X, Zhang J, Arfuso F, Chinnathambi A, Zayed ME, Alharbi SA, Kumar AP, Ahn KS, Sethi G.. Targeting TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor by natural products as a potential therapeutic approach for cancer therapy. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(6):760–14. doi:10.1177/1535370215579167. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
