The Role of Interferon-α in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36776068
- PMCID: PMC10473139
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-221081
The Role of Interferon-α in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) impose significant financial and healthcare burden on populations all over the world. The prevalence and incidence of NDs have been observed to increase dramatically with age. Hence, the number of reported cases is projected to increase in the future, as life spans continues to rise. Despite this, there is limited effective treatment against most NDs. Interferons (IFNs), a family of cytokines, have been suggested as a promising therapeutic target for NDs, particularly IFN-α, which governs various pathological pathways in different NDs.
Objective: This systematic review aimed to critically appraise the currently available literature on the pathological role of IFN-α in neurodegeneration/NDs.
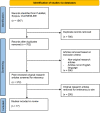
Methods: Three databases, Scopus, PubMed, and Ovid Medline, were utilized for the literature search.
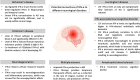
Results: A total of 77 journal articles were selected for critical evaluation, based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The studies selected and elucidated in this current systematic review have showed that IFN-α may play a deleterious role in neurodegenerative diseases through its strong association with the inflammatory processes resulting in mainly neurocognitive impairments. IFN-α may be displaying its neurotoxic function via various mechanisms such as abnormal calcium mineralization, activation of STAT1-dependent mechanisms, and increased quinolinic acid production.
Conclusion: The exact role IFN-α in these neurodegenerative diseases have yet to be determine due to a lack in more recent evidence, thereby creating a variability in the role of IFN-α. Future investigations should thus be conducted, so that the role played by IFN-α in neurodegenerative diseases could be delineated.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; dementia; interferon-alpha; multiple sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures

References
-
- Kouli A, Torsney KM, Kuan WL (2018) Parkinson’s disease: Etiology, neuropathology, and pathogenesis. s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects, Stoker TB, Greenland JC, eds. Codon Publications, Brisbane. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Sidhu J, Goyal A, Tsao JW (2021) Alzheimer disease. In StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island. StatPearls.
-
- Kowal SL, Dall TM, Chakrabarti R, Storm MV, Jain A (2013) The current and projected economic burden of Parkinson’s disease in the United States. Mov Disord 28, 311–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

