Impact of the development of information society on healthcare efficiency: Empirical evidence from 31 Chinese provinces
- PMID: 36776406
- PMCID: PMC9912566
- DOI: 10.1177/20552076231154375
Impact of the development of information society on healthcare efficiency: Empirical evidence from 31 Chinese provinces
Abstract
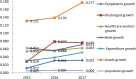
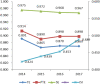
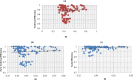
The development of information society has deeply changed the style of the healthcare service delivery and medical information access. This study aims to investigate how the information society development affects the efficiency of healthcare system in China, and explore provincial disparities in the impact. Based on the two-stage Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) framework, this paper uses a panel data from 31 Chinese provinces from 2014 to 2017 to estimate efficiency of healthcare service and analyze the influence of the development of information society on efficiency. With the information society index (ISI) increased from 0.423 to 0.488 during the sample period, the healthcare efficiency experienced a slight decrease from 0.892 to 0.869. Moreover, the pure technical efficiency (PTE) is much lower than the scale efficiency (SE), and thus is the key to enhance the overall technical efficiency (TE). The time-fixed Tobit regression analysis suggests that information society development leads to a significant increase in PTE, but results in a decrease in SE, and therefore has little effect on TE. Further analysis reveals that the impact differs sharply between low-efficiency and high-efficiency provinces. For the low-efficiency provinces, the TE increases significantly with the development of the information society, mainly due to a considerable increase in PTE. In contrast, the TE decreases for the high-efficiency provinces, mainly caused by a decrease in SE. This paper highlights the importance of information infrastructure investment in healthcare system and the application of emerging information technologies to breakout the time and space boundaries of healthcare services in improving overall efficiency. In inefficient provinces, it is also necessary to properly control the growth of healthcare inputs.
Keywords: DEA; Tobit model; healthcare efficiency; healthcare service; information society.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Technical efficiency of provincial public healthcare in South Africa.Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2020 Jan 28;18:3. doi: 10.1186/s12962-020-0199-y. eCollection 2020. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2020. PMID: 32002018 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Operational Efficiency and Quality of Tertiary Hospitals in Taiwan: The Application of the EBITDA Indicator to the DEA Method and TOBIT Regression.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;10(1):58. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10010058. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052222 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the efficiency of health resource allocation in the western region of China-based on three-stage DEA and Tobit regression analysis.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Apr 1;25(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12630-y. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40165157 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency and productivity measurement of rural township hospitals in China: a bootstrapping data envelopment analysis.BMJ Open. 2016 Nov 11;6(11):e011911. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011911. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27836870 Free PMC article.
-
The use of Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) in healthcare with a focus on hospitals.Health Care Manag Sci. 2019 Jun;22(2):245-286. doi: 10.1007/s10729-018-9436-8. Epub 2018 Feb 24. Health Care Manag Sci. 2019. PMID: 29478088 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Broadband Infrastructure Construction on Medical Resource Mismatch: Quasi-Natural Experiment From the Broadband China Policy.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Mar 21;26:e53921. doi: 10.2196/53921. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 38512327 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency evaluation, regional technological heterogeneity and determinant of total factor productivity change in China's healthcare system.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 23;14(1):19606. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70736-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39179793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peng J, Li S, Wang Y. Spatial relevance research on regional informatization and green economy development—an empirical analysis based on the spatial Dubin model. Journal of Industrial Technological Economics 2019; 38(08): 99–107.
-
- China National Information Centre. 2017 Global and China Information Society Development Report. http://wwwsicgovcn/News/566/8728htm. 2018.
-
- Kraus S, Schiavone F, Pluzhnikova Aet al. et al. Digital transformation in healthcare: analyzing the current state-of-research. J Bus Res 2021; 123: 557–567.
-
- Almalki ZS, Simsim DA. The Role of Health Technology in Transforming Healthcare Delivery and Enhancing Spending Efficiency. Glob J Med Res 2020; 2(3): 11–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

