Risk of Uveitis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease on Immunosuppressive Drug Therapy
- PMID: 36776495
- PMCID: PMC9802084
- DOI: 10.1093/crocol/otaa041
Risk of Uveitis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease on Immunosuppressive Drug Therapy
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients may develop anterior uveitis.
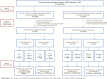
Methods: An observational cohort of IBD patients followed new users of (1) tumor necrosis factor inhibitor versus nonbiologic agents or (2) adalimumab versus infliximab until occurrence of anterior uveitis or treatment change/discontinuation. Cox-proportional hazards models estimated hazard ratios in propensity score-matched cohorts of Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis patients.
Results: No statistically significant differences in the risk of uveitis were observed between initiators of nonbiologics and tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Effect estimates for adalimumab versus infliximab were highly imprecise due to limited outcomes.
Conclusions: Uveitis risk was not different between IBD patients treated with immunosuppressives.
Keywords: adalimumab; inflammatory bowel disease; infliximab; uveitis.
© 2020 Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn's & Colitis Foundation.
Figures

References
-
- Loftus EV Jr. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1504–1517. - PubMed
-
- Kappelman MD, Rifas–Shiman SL, Kleinman K, et al. . The prevalence and geographic distribution of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5:1424–9. - PubMed
-
- Burisch J, Jess T, Martinato M, et al. ; ECCO-EpiCom . The burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Europe. J Crohns Colitis 2013;7:322–337. - PubMed
-
- Longobardi T, Jacobs P, Wu L, Bernstein CN. Work losses related to inflammatory bowel disease in Canada: results from a National Population Health Survey. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:844–849. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
