The Altmetric Attention Score Is Associated With Citation Rates and May Reflect Academic Impact in the Total Joint Arthroplasty Literature
- PMID: 36776509
- PMCID: PMC9837400
- DOI: 10.1177/15563316221115723
The Altmetric Attention Score Is Associated With Citation Rates and May Reflect Academic Impact in the Total Joint Arthroplasty Literature
Abstract
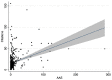
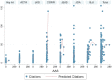
Background: Given the increasing interest and potential use of social media for the promotion of orthopedic literature, there is a need to better understand Altmetrics. Purposes: We sought to determine the relationship between the Altmetric Attention Score (AAS) and the number of citations for articles on total joint arthroplasty (TJA) published in orthopedics journals. We also sought to determine the predictors of greater social media attention for these articles. Methods: Articles on TJA published in Bone and Joint Journal (BJJ), Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (JBJS), Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research (CORR), Journal of Arthroplasty, Journal of Knee Surgery, Hip International, and Acta Orthopaedica in 2016 were extracted (n = 498). One-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni corrections was used to compare AAS and citations across journals. Multivariate regressions were used to determine predictors of social media attention and number of citations. Results: The mean AAS and number of citations were 7.5 (range: 0-289) and 16.7 (range: 0-156), respectively. Significant between-group effects were observed according to journal for AAS and number of citations. Publishing an article in JBJS was the strongest predictor of higher number of citations. Publishing an article in BJJ was the only independent predictor of higher AAS, while publishing an article in JBJS or CORR trended toward statistical significance. A higher AAS was a significant predictor of a higher number of citations. Number of citations and number of study references were positive predictors of greater social media attention on Twitter and Facebook. Conclusions: In articles on TJA published in 7 journals in 2016, a higher AAS was a associated with a higher number of citations. Various bibliometric characteristics were found to be significantly associated with greater social media attention; the most common influences were number of citations and number of references. Researchers in orthopedics can use this information when considering how to assess the impact of their work.
Keywords: Altmetrics; arthroplasty; bibliometrics; citations; hip; knee; social media.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: CAH reports relationships with CD diagnostics, Cymedica, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, KCI, Lyfstone, OREF, Orthofix, PSI, Stryker, and Zimmer. AS reports relationships with Zimmer Biomet, Intellijoint, AZ Solutions, and ROMTech. JC reports relationships with Arthrex, CONMED Linvatec, Ossur, and Smith & Nephew. NSP reports relationships with RegenLab and Zimmer. The other authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aksnes DW, Langfeldt L, Wouters P. Citations, citation indicators, and research quality: An overview of basic concepts and theories. SAGE Open. 2019;9:2158244019829575. 10.1177/2158244019829575. - DOI
-
- Altmetric. Bookmarklet for researchers. Available at: https://www.altmetric.com/products/free-tools/bookmarklet/. Accessed June 28, 2022.
-
- Altmetric. How is the Altmetric Attention Score calculated? Available at: https://help.altmetric.com/support/solutions/articles/6000233311-how-is-.... Accessed July 22, 2022.
-
- Altmetric. What is Altmetrics and what does it provide? Available at: https://help.altmetric.com/support/solutions/articles/6000232837-what-is.... Accessed June 28, 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

