1,1-Difluoroethane Hydrocarbon Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 36776796
- PMCID: PMC9911916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2022.101716
1,1-Difluoroethane Hydrocarbon Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
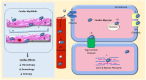
1,1-Difluoroethane (DFE) cardiomyopathy results from the direct inhalation of toxic halogenated hydrocarbons. We present a case series of acute DFE cardiomyopathy illustrating the typical presentation of severe DFE cardiomyopathy along with a detailed description of its mechanism of injury. (Level of Difficulty: Advanced.).
Keywords: 1,1-difluoroethane hydrocarbon; DFE, 1,1-difluoroethane; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; EF, ejection fraction; huffing; nonischemic cardiomyopathy; toxic cardiomyopathy.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson C.E., Loomis G.A. Recognition and prevention of inhalant abuse. Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(5):869–874. - PubMed
-
- Gummin D.D., Mowry J.B., Beuhler M.C., et al. Annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers' National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th annual report. Clin Toxicol. 2021;59(12):1282–1501. - PubMed
-
- Tormoehlen L.M., Tekulve K.J., Nanagas K.A. Hydrocarbon toxicity: a review. Clin Toxicol. 2014;52(5):479–489. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention High School Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance - United States 2019. https://nccd.cdc.gov/Youthonline/App/Results
-
- Fogelson B., Qu D., Bhagat M., et al. Multiorgan system failure secondary to difluoroethane toxicity in a patient “huffing” air duster: a case report. J Addict Dis. 2022;19:1–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

