Quantum sensors for biomedical applications
- PMID: 36776813
- PMCID: PMC9896461
- DOI: 10.1038/s42254-023-00558-3
Quantum sensors for biomedical applications
Abstract
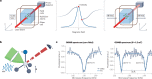
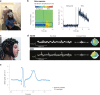
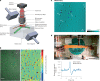
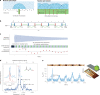
Quantum sensors are finding their way from laboratories to the real world, as witnessed by the increasing number of start-ups in this field. The atomic length scale of quantum sensors and their coherence properties enable unprecedented spatial resolution and sensitivity. Biomedical applications could benefit from these quantum technologies, but it is often difficult to evaluate the potential impact of the techniques. This Review sheds light on these questions, presenting the status of quantum sensing applications and discussing their path towards commercialization. The focus is on two promising quantum sensing platforms: optically pumped atomic magnetometers, and nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond. The broad spectrum of biomedical applications is highlighted by four case studies ranging from brain imaging to single-cell spectroscopy.
Keywords: Confocal microscopy; Imaging and sensing; Nanosensors; Quantum metrology; Solution-state NMR.
© Springer Nature Limited 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare the following competing interests: R.L.W., M.D.L. and H.P. are scientific co-founders of QDTI Inc.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
