Efficacy of interferon alpha for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36776844
- PMCID: PMC9909279
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1069894
Efficacy of interferon alpha for the treatment of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: IFN-α intervention may block SARS-CoV-2 replication and normalize the deregulated innate immunity of COVID-19.
Aim: This meta-analysis aimed to investigate the efficacy of interferon IFN-α-containing regimens when treating patients with moderate-to-severe COVID-19.
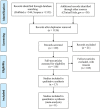
Material and methods: PubMed, SCOPUS, and ClinicalTrials.gov were searched from inception to 15 January 2022. A systematic literature search was conducted by applying relevant terms for 'COVID-19' and 'interferon-α'. The primary outcome enclosed the all-cause hospital mortality. The secondary outcomes constituted the length of hospital stay; hospital discharge; nucleic acid negative conversion.
Results: Eleven studies are enclosed in the meta-analysis. No significant difference in the all-cause mortality rate was found between the study and control groups (OR 0.2; 95% CI 0.05-1.2; I2 = 96%). The implementation of interferon did not influence such outcomes as the length of hospital stay (OR 0.9; 95% CІ, 0.3-2.6; I2 = 91%), nucleic acid negative conversion (OR 0.8; 95% CI, 0.04-17.2; I2 = 94%). Nevertheless, IFN-α treatment resulted in a higher number of patients discharged from the hospital (OR 26.6; 95% CІ, 2.7-254.3; I2 = 95%).
Conclusions: Thus, IFN-α does not benefit the survival of hospitalized COVID-19 patients but may increase the number of patients discharged from the hospital.
Systematic review registration: www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero, identifier (CRD42022374589).
Keywords: COVID-19; IFN-α; SARS-CoV-2; interferon-α; mortality.
Copyright © 2023 Buchynskyi, Kamyshna, Lyubomirskaya, Moshynets, Kobyliak, Oksenych and Kamyshnyi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of interferon-β-containing regimens in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022 May;20(5):741-747. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2022.2004118. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022. PMID: 34747295 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a genetically engineered interferon-alpha versus traditional interferon-alpha in the treatment of moderate-to-severe COVID-19: a randomised clinical trial.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):391-401. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1890329. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 33620016 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
No Statistically Apparent Difference in Antiviral Effectiveness Observed Among Ribavirin Plus Interferon-Alpha, Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha, and Ribavirin Plus Lopinavir/Ritonavir Plus Interferon-Alpha in Patients With Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results of a Randomized, Open-Labeled Prospective Study.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1071. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01071. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32765274 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Interferon-β in Moderate-to-Severe Hospitalised Cases of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Drug Investig. 2021 Dec;41(12):1037-1046. doi: 10.1007/s40261-021-01092-9. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Clin Drug Investig. 2021. PMID: 34687413 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the management of knee osteoarthritis: a narrative review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 21;12:1523027. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1523027. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39906596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the gut-liver axis: microbial contributions to the pathogenesis of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.Front Microbiol. 2025 Apr 25;16:1577724. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1577724. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40351307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and Biochemical Mechanisms of Cardiomyopathy Development Following Prenatal Hypoxia-Focus on the NO System.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 16;14(6):743. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060743. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effectiveness of Interferon-α2b against COVID-19 with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: The Ukrainian Experience.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6887. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086887. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108051 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation on COVID-19 outcomes: an umbrella review of systematic reviews.Front Nutr. 2025 Jun 13;12:1559471. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1559471. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40584095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update (2022). Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

