Inflammation balance in skeletal muscle damage and repair
- PMID: 36776867
- PMCID: PMC9909416
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1133355
Inflammation balance in skeletal muscle damage and repair
Abstract
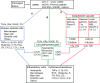
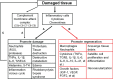
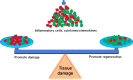
Responding to tissue injury, skeletal muscles undergo the tissue destruction and reconstruction accompanied with inflammation. The immune system recognizes the molecules released from or exposed on the damaged tissue. In the local minor tissue damage, tissue-resident macrophages sequester pro-inflammatory debris to prevent initiation of inflammation. In most cases of the skeletal muscle injury, however, a cascade of inflammation will be initiated through activation of local macrophages and mast cells and recruitment of immune cells from blood circulation to the injured site by recongnization of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and activated complement system. During the inflammation, macrophages and neutrophils scavenge the tissue debris to release inflammatory cytokines and the latter stimulates myoblast fusion and vascularization to promote injured muscle repair. On the other hand, an abundance of released inflammatory cytokines and chemokines causes the profound hyper-inflammation and mobilization of immune cells to trigger a vicious cycle and lead to the cytokine storm. The cytokine storm results in the elevation of cytolytic and cytotoxic molecules and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the damaged muscle to aggravates the tissue injury, including the healthy bystander tissue. Severe inflammation in the skeletal muscle can lead to rhabdomyolysis and cause sepsis-like systemic inflammation response syndrome (SIRS) and remote organ damage. Therefore, understanding more details on the involvement of inflammatory factors and immune cells in the skeletal muscle damage and repair can provide the new precise therapeutic strategies, including attenuation of the muscle damage and promotion of the muscle repair.
Keywords: complements; damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMP); immune cell; inflammation; sepsis; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2023 Tu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptors in sepsis-associated cytokine storm and their endogenous negative regulators as future immunomodulatory targets.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt B):107087. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107087. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33075714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) induces acute severe lung inflammation via IL-1 causing cytokine storm in COVID-19: a promising inhibitory strategy.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 Nov-Dec;34(6):1971-1975. doi: 10.23812/20-1-E. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 33016027
-
The inflammatory response to skeletal muscle injury: illuminating complexities.Sports Med. 2008;38(11):947-69. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200838110-00005. Sports Med. 2008. PMID: 18937524 Review.
-
Macrophages play an essential role in trauma-induced sterile inflammation and tissue repair.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018 Jun;44(3):335-349. doi: 10.1007/s00068-018-0956-1. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2018. PMID: 29666944 Review.
-
The Transcription Factor Mohawk Facilitates Skeletal Muscle Repair via Modulation of the Inflammatory Environment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 4;25(9):5019. doi: 10.3390/ijms25095019. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732238 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Perinatal Stem Cell Secretome as Potential Therapy for Muscular Dystrophies.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 13;13(2):458. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020458. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Hormonal and Inflammatory Responses following Lower and Upper Body Resistance Exercises Performed to Volitional Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 7;25(13):7455. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137455. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000562 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gut microbes-muscle axis in muscle function and meat quality.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Apr 8. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2885-4. Online ahead of print. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40220074 Review.
-
Immune Dysregulation in Depression and Anxiety: A Review of the Immune Response in Disease and Treatment.Cells. 2025 Apr 17;14(8):607. doi: 10.3390/cells14080607. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40277932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations of tissue damage induced inflammatory plasticity in masseter muscle with the resolution of chronic myalgia.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 12;13(1):22057. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49280-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38086903 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

