Factors affecting IgG4-mediated complement activation
- PMID: 36776883
- PMCID: PMC9910309
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1087532
Factors affecting IgG4-mediated complement activation
Abstract
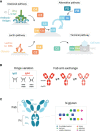
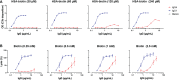
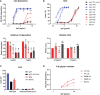
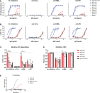
Of the four human immunoglobulin G (IgG) subclasses, IgG4 is considered the least inflammatory, in part because it poorly activates the complement system. Regardless, in IgG4 related disease (IgG4-RD) and in autoimmune disorders with high levels of IgG4 autoantibodies, the presence of these antibodies has been linked to consumption and deposition of complement components. This apparent paradox suggests that conditions may exist, potentially reminiscent of in vivo deposits, that allow for complement activation by IgG4. Furthermore, it is currently unclear how variable glycosylation and Fab arm exchange may influence the ability of IgG4 to activate complement. Here, we used well-defined, glyco-engineered monoclonal preparations of IgG4 and determined their ability to activate complement in a controlled system. We show that IgG4 can activate complement only at high antigen and antibody concentrations, via the classical pathway. Moreover, elevated or reduced Fc galactosylation enhanced or diminished complement activation, respectively, with no apparent contribution from the lectin pathway. Fab glycans slightly reduced complement activation. Lastly, we show that bispecific, monovalent IgG4 resulting from Fab arm exchange is a less potent activator of complement than monospecific IgG4. Taken together, these results imply that involvement of IgG4-mediated complement activation in pathology is possible but unlikely.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; antibodies; complement activation; fab arm exchange; glycoengineering; primary membranous nephropathy.
Copyright © 2023 Oskam, Damelang, Streutker, Ooijevaar-de Heer, Nouta, Koeleman, Van Coillie, Wuhrer, Vidarsson and Rispens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Alternative Pathway Is Necessary and Sufficient for Complement Activation by Anti-THSD7A Autoantibodies, Which Are Predominantly IgG4 in Membranous Nephropathy.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 7;13:952235. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.952235. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874690 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunobiology of Immunoglobulin G4 and Complement Activation Pathways in IgG4-Related Disease.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017;401:61-73. doi: 10.1007/82_2016_39. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27726003 Review.
-
Altered glycosylation of IgG4 promotes lectin complement pathway activation in anti-PLA2R1-associated membranous nephropathy.J Clin Invest. 2021 Mar 1;131(5):e140453. doi: 10.1172/JCI140453. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33351779 Free PMC article.
-
Possible participation of IgG4 in the activation of complement in IgG4-related disease with hypocomplementemia.Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(2):251-8. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1076924. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Mod Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26357950
-
IgG4 Subclass of Immunoglobulins; Immunobiology and Roles in Relation to Human Diseases.Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2024;67(4):101-106. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2025.6. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2024. PMID: 40179839 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunoglobulin G4 in primary Sjögren's syndrome and IgG4-related disease - connections and dissimilarities.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 19;15:1376723. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1376723. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39364411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgG subclass shifts occurring at acute exacerbations in autoimmune nodopathies.J Neurol. 2024 Sep;271(9):6301-6312. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12597-6. Epub 2024 Aug 2. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39093334
-
Optimized Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Anti-PEG Antibody Detection in Healthy Donors and Patients Treated with PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin.Mol Pharm. 2024 Jun 3;21(6):3053-3060. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00278. Epub 2024 May 14. Mol Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38743264 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of immunoglobulin G oligomerization by variable domain glycans: A mechanism to regulate complement activation.PNAS Nexus. 2025 Jul 16;4(7):pgaf216. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf216. eCollection 2025 Jul. PNAS Nexus. 2025. PMID: 40735689 Free PMC article.
-
IgG4 autoantibodies and autoantigens in the context of IgG4-autoimmune disease and IgG4-related disease.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 16;15:1272084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1272084. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38433835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

