Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum S100B in sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36776893
- PMCID: PMC9911439
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1102126
Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum S100B in sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: In sepsis, brain dysfunction is known as Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE), which often results in severe cognitive and neurological sequelae and increases the risk of death. Our systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to explore the diagnostic and prognostic value of serum S100 calcium-binding protein B (S100B) in SAE patients.
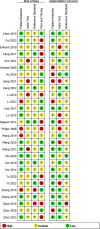
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of the databases PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane databases, CNKI, VIP, and WFSD from their inception dates until August 20, 2022. A Meta-analysis of the included studies was also performed using Review Manager version 5.4 and Stata16.0.
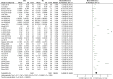
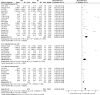
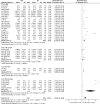
Results: This meta-analysis included 28 studies with 1401 serum samples from SAE patients and 1591 serum samples from no-encephalopathy septic (NE) patients. The Meta-Analysis showed that individuals with SAE had higher serum S100B level than NE controls (MD, 0.49 [95% CI (0.37)-(0.60), Z =8.29, P < 0.00001]), and the baseline level of serum S100B in septic patients with burn was significantly higher than average (1.96 [95% CI (0.92)-(2.99), Z =3.71, P < 0.0002]) In addition, septic patients with favorable outcomes had lower serum S100B levels than those with unfavorable outcomes (MD, -0.35 [95% CI (-0.50)-(-0.20), Z =4.60, P < 0.00001]).
Conclusion: Our Meta-Analysis indicates that higher serum S100B level in septic patients are moderately associated with SAE and unfavorable outcomes (The outcomes here mainly refer to the mortality). The serum S100B level may be a useful diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of SAE.
Keywords: S100B; biomarker; meta-analysis; outcome; sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
Copyright © 2023 Hu, Xie, Li and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of evaluating neuron specific enolase as a serum biomarker for sepsis-associated encephalopathy.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Apr 20;131:111857. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111857. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38489973
-
Unveiling neurogenic biomarkers for the differentiation between sepsis patients with or without encephalopathy: an updated meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 8;14(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13643-025-02784-5. Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39923061 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of serum neuron-specific enolase in sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 22;13(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02583-4. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39039544 Free PMC article.
-
Can serum NSE predict and evaluate sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Neurosci. 2024 Jun;124:150-153. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2024.04.029. Epub 2024 May 7. J Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38718610 Review.
-
Diagnostic value of NT-proCNP compared to NSE and S100B in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of patients with sepsis-associated encephalopathy.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Jan 23;692:167-173. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.11.014. Epub 2018 Nov 10. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30423400
Cited by
-
Improved prediction of sepsis-associated encephalopathy in intensive care unit sepsis patients with an innovative nomogram tool.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 20;15:1344004. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1344004. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38445262 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the prognosis in patients with sepsis by an endoplasmic reticulum stress gene signature.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Nov 25;15(22):13434-13451. doi: 10.18632/aging.205252. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 38011291 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of the Chinese herbal medicine Jintiange capsules in the postoperative treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 15;10:1289818. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1289818. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38162884 Free PMC article.
-
S100B Serum Levels in Chronic Heart Failure Patients: A Multifaceted Biomarker Linking Cardiac and Cognitive Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9094. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169094. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201780 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of the lactate-to-albumin ratio in assessing prognosis in critically ill patients with sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A retrospective analysis.Sci Prog. 2025 Jul-Sep;108(3):368504251371107. doi: 10.1177/00368504251371107. Epub 2025 Aug 18. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40827023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. . Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet (London England) (2020) 395(10219):200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

