PSMA1, a Poor Prognostic Factor, Promotes Tumor Growth in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 36776923
- PMCID: PMC9918360
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/5386635
PSMA1, a Poor Prognostic Factor, Promotes Tumor Growth in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
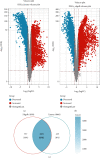
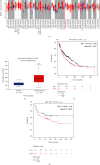
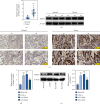
Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) has a poor clinical prognosis and lacks effective targeted therapy. This study is aimed at investigating the role of PSMA1 (proteasome subunit alpha type-1) in LUSC. The differential expression genes (DEGs) in LUSC were retrieved from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) by "edgR" algorithm and by "limma" R package. Then, the relationship between genes and overall survival (OS) was explored by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and multivariate Cox (multi-Cox) regression. Next, the PSMA1 expression in tissues of LUSC was detected by IHC, qRT-PCR, and western blot (WB). Moreover, the effects of PSMA1 on the proliferation and viability of LUSC cell were explored by cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8) assays, colony formation assays, and flow cytometry (FCM) analysis. All 4421 DEGs were screened by TCGA database, and 26 genes associated with OS were selected by multi-Cox. Based on TCGA database, PSMA1 was highly expressed in tissues of LUSC patients, and OS and FP of patients with PSMA1 overexpression were significantly lower than those of patients with low PSMA1 expression. Furthermore, PSMA1 knockdown significantly decreased the proliferation of LUSC cells and promoted the apoptosis of LUSC cells, and these effects were reversed by PSMA1 overexpression. The results of this project supported that PSMA1 might be a critical gene regulating the development of LUSC and has the potential to be explored as a prognostic biomarker of LUSC.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of specific prognostic markers for lung squamous cell carcinoma based on tumor progression, immune infiltration, and stem index.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 29;14:1236444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1236444. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37841237 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Validation of Prognostic Regulation Network Based on RNA-Binding Protein Genes in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma.DNA Cell Biol. 2021 Dec;40(12):1563-1583. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0145. DNA Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34931870
-
DNA damage repair gene signature model for predicting prognosis and chemotherapy outcomes in lung squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Aug 8;22(1):866. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09954-x. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35941578 Free PMC article.
-
FUBP1 promotes the proliferation of lung squamous carcinoma cells and regulates tumor immunity through PD-L1.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2022 Sep 1;50(5):68-74. doi: 10.15586/aei.v50i5.659. eCollection 2022. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2022. PMID: 36086966
-
CHMP4C regulates lung squamous carcinogenesis and progression through cell cycle pathway.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Aug;13(8):4762-4774. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-583. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 34527317 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aberrated PSMA1 expression associated with clinicopathological features and prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Odontology. 2024 Jul;112(3):950-958. doi: 10.1007/s10266-023-00883-0. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Odontology. 2024. PMID: 38216818
-
Iron Supplementation Increases Tumor Burden and Alters Protein Expression in a Mouse Model of Human Intestinal Cancer.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 27;16(9):1316. doi: 10.3390/nu16091316. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38732562 Free PMC article.
-
Acute-phase plasma proteomics of rabbit lung VX2 tumors treated by image-guided microwave ablation.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 26;14:1435256. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1435256. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39252952 Free PMC article.
-
Clinically relevant stratification of lung squamous carcinoma patients based on ubiquitinated proteasome genes for 3P medical approach.EPMA J. 2024 Mar 4;15(1):67-97. doi: 10.1007/s13167-024-00352-w. eCollection 2024 Mar. EPMA J. 2024. PMID: 38463626 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-1976 affects lung squamous cell carcinoma development by targeting NCAPH.J Appl Genet. 2025 Jul 23. doi: 10.1007/s13353-025-00990-4. Online ahead of print. J Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 40699282
References
-
- Xia L., Yu Y., Lan F., et al. Case report: tumor microenvironment characteristics in a patient with HER2 mutant lung squamous cell carcinoma harboring high PD-L1 expression who presented hyperprogressive disease. Frontiers in Oncology . 2021;11, article 760703 doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.760703. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

