4-Methoxydalbergione Elicits Anticancer Effects by Upregulation of GADD45G in Human Liver Cancer Cells
- PMID: 36776954
- PMCID: PMC9908360
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6710880
4-Methoxydalbergione Elicits Anticancer Effects by Upregulation of GADD45G in Human Liver Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background: 4-Methoxydalbergione (4MOD) is a flavonoid isolated from the heartwood of Dalbergia. Studies have demonstrated that 4MOD exerts anticancer activities on bladder cancer and astrocytoma. However, the anticancer activity of 4MOD in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unknown. This study aims to examine its anticancer activities and mechanisms in human liver cancer cells.
Methods: CCK-8, colony forming, wound healing, transwell migration, and AnnexinV/PI assays were used to assess the anticancer effects of 4MOD in HCC cells. RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) was selected to explore the possible mechanisms underlying the anti-HCC activity of 4MOD. The mRNA expression levels of target genes were verified through quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). A lentiviral shRNA interference technique was used to silence GADD45G expression. GADD45G knockdown was employed to confirm the crucial role of GADD45G in the 4MOD-mediatedanti-HCC effects.
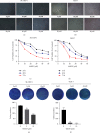
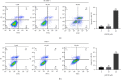
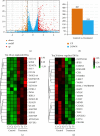
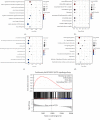
Results: 4MOD inhibited HCC cells' proliferation and migration and promoted tumor cell apoptosis. RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR analyses revealed that 4MOD treatment increased GADD45G expression. Silencing GADD45G reversed 4MOD-mediated inhibition of proliferation, migration, and promotion of apoptosis.
Conclusions: Our findings show that 4MOD elicits anti-HCC effects by upregulating GADD45G expression and could be a valuable anticancer agent for liver cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Liping Zeng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identify GADD45G as a potential target of 4-methoxydalbergione in treatment of liver cancer: bioinformatics analysis and in vivo experiment.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Oct 13;21(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03214-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37833694 Free PMC article.
-
4-Methoxydalbergione Inhibits Bladder Cancer Cell Growth via Inducing Autophagy and Inhibiting Akt/ERK Signaling Pathway.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 16;8:789658. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.789658. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35252345 Free PMC article.
-
4-Methoxydalbergione is a potent inhibitor of human astroglioma U87 cells in vitro and in vivo.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Sep;42(9):1507-1515. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-00560-w. Epub 2020 Dec 11. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 33311599 Free PMC article.
-
SIP1 is a downstream effector of GADD45G in senescence induction and growth inhibition of liver tumor cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 20;6(32):33636-47. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5602. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26378039 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of lncRNA NIFK-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma by m6A methylation promotes disease progression and sorafenib resistance.Hum Cell. 2021 Nov;34(6):1800-1811. doi: 10.1007/s13577-021-00587-z. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Hum Cell. 2021. PMID: 34374933 Review.
Cited by
-
4‑Methoxydalbergione inhibits the tumorigenesis and metastasis of lung cancer through promoting ferroptosis via the DNMT1/system Xc‑/GPX4 pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jan;31(1):19. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13384. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39513605 Free PMC article.
-
Identify GADD45G as a potential target of 4-methoxydalbergione in treatment of liver cancer: bioinformatics analysis and in vivo experiment.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Oct 13;21(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03214-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37833694 Free PMC article.
-
A gene signature associated with cellular senescence serves as an important prognostic indicator in hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 30;14(3):2054-2065. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-335. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40224975 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

