Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) exposure in relation to the kidneys: A review of current available literature
- PMID: 36776978
- PMCID: PMC9909492
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1103141
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) exposure in relation to the kidneys: A review of current available literature
Abstract
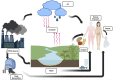
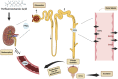
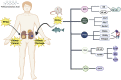
Perfluorooctanoic acid is an artificial and non-degradable chemical. It is widely used due to its stable nature. It can enter the human body through food, drinking water, inhalation of household dust and contact with products containing perfluorooctanoic acid. It accumulates in the human body, causing potential harmful effects on human health. Based on the biodegradability and bioaccumulation of perfluorooctanoic acid in the human body, there are increasing concerns about the adverse effects of perfluorooctanoic acid exposure on kidneys. Research shows that kidney is the main accumulation organ of Perfluorooctanoic acid, and Perfluorooctanoic acid can cause nephrotoxicity and produce adverse effects on kidney function, but the exact mechanism is still unknown. In this review, we summarize the relationship between Perfluorooctanoic acid exposure and kidney health, evaluate risks more clearly, and provide a theoretical basis for subsequent research.
Keywords: CKD; EGFR; PFAS; kidney; perfluorooctanoic acid; pfoa; renal tumors.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Yan, Wang, Chen, Liu, Cui, Liang, Ren and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Health-related toxicity of emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances: Comparison to legacy PFOS and PFOA.Environ Res. 2022 Sep;212(Pt C):113431. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113431. Epub 2022 May 13. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35569538 Review.
-
Risk assessment for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in air, blood serum and water: mortality from liver and kidney disease.Occup Environ Med. 2024 Aug 16;81(7):373-380. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2023-109228. Occup Environ Med. 2024. PMID: 39025495
-
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), an emerging drinking water contaminant: a critical review of recent literature.Environ Res. 2012 Jul;116:93-117. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 May 4. Environ Res. 2012. PMID: 22560884 Review.
-
Human exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through drinking water: A review of the recent scientific literature.Environ Res. 2019 Oct;177:108648. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.108648. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Environ Res. 2019. PMID: 31421451 Review.
Cited by
-
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances as forever chemicals in drinking water: Unraveling the nexus with obesity and endocrine disruption - A mini review.Heliyon. 2025 Feb 18;11(4):e42782. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42782. eCollection 2025 Feb 28. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 40066031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Combined Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Metals with Chronic Kidney Disease.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Apr 11;21(4):468. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21040468. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38673379 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Resveratrol Against Perfluorooctanoic Acid-Induced Testicular and Epididymal Toxicity in Adult Rats Exposed During Their Prepubertal Period.Toxics. 2025 Jan 29;13(2):111. doi: 10.3390/toxics13020111. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 39997926 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of the occurrence, detection, and ecotoxicity studies of perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in aqueous environments.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2025 Feb 25;23(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s40201-025-00934-4. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40018265 Review.
-
Towards a Better Understanding of the Human Health Risk of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Using Organoid Models.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Apr 7;12(4):393. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12040393. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40281753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott B. D., Wood C. R., Watkins A. M., Tatum-Gibbs K., Das K. P., Lau C. (2012). Effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) on expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) and nuclear receptor-regulated genes in fetal and postnatal CD-1 mouse tissues. Reprod. Toxicol. 33 (4), 491–505. 10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.11.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous