A Pipeline for the Development of Microsatellite Markers using Next Generation Sequencing Data
- PMID: 36777003
- PMCID: PMC9878831
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202923666220428101350
A Pipeline for the Development of Microsatellite Markers using Next Generation Sequencing Data
Abstract
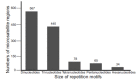
Background: Also known as Simple Sequence Repetitions (SSRs), microsatellites are profoundly informative molecular markers and powerful tools in genetics and ecology studies on plants. Objective: This research presents a workflow for developing microsatellite markers using genome skimming. Methods: The pipeline was proposed in several stages that must be performed sequentially: obtaining DNA sequences, identifying microsatellite regions, designing primers, and selecting candidate microsatellite regions to develop the markers. Our pipeline efficiency was analyzed using Illumina sequencing data from the non-model tree species Pterodon emarginatus Vog. Results: The pipeline revealed 4,382 microsatellite regions and drew 7,411 pairs of primers for P. emarginatus. However, a much larger number of microsatellite regions with the potential to develop markers were discovered from our pipeline. We selected 50 microsatellite regions with high potential for developing markers and organized 29 microsatellite regions in sets for multiplex PCR. Conclusion: The proposed pipeline is a powerful tool for fast and efficient development of microsatellite markers on a large scale in several species, especially nonmodel plant species.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; PCR multiplex; Pterodon emarginatus; genome skimming; microsatellite markers; primer design.
© 2022 Bentham Science Publishers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lessons learned from microsatellite development for nonmodel organisms using 454 pyrosequencing.J Evol Biol. 2013 Mar;26(3):600-11. doi: 10.1111/jeb.12077. Epub 2013 Jan 17. J Evol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23331991
-
Development and validation of microsatellite markers for Brachiaria ruziziensis obtained by partial genome assembly of Illumina single-end reads.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jan 16;14:17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-17. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23324172 Free PMC article.
-
A Galaxy-based bioinformatics pipeline for optimised, streamlined microsatellite development from Illumina next-generation sequencing data.Conserv Genet Resour. 2016;8(4):481-486. doi: 10.1007/s12686-016-0570-7. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Conserv Genet Resour. 2016. PMID: 32355508 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale identification of polymorphic microsatellites using an in silico approach.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Sep 15;9:374. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-374. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18793407 Free PMC article.
-
Using next-generation sequencing approaches to isolate simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci in the plant sciences.Am J Bot. 2012 Feb;99(2):193-208. doi: 10.3732/ajb.1100394. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Am J Bot. 2012. PMID: 22186186 Review.
References
-
- Teshome Z., Terfa M.T., Tesfaye B., Shiferaw E., Olango T.M. Genetic diversity in anchote (Coccinia abyssinica (Lam.) Cogn) using microsatellite markers. Curr. Plant Biol. 2020;24:100167. doi: 10.1016/j.cpb.2020.100167. - DOI
-
- Kumar C., Kumar R., Singh S.K., Goswami A.K., Nagaraja A., Paliwal R., Singh R. Development of novel g-SSR markers in guava (Psidium guajava L.) cv. Allahabad Safeda and their application in genetic diversity, population structure and cross species transferability studies. PLoS One. 2020;15(8):e0237538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237538. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
