Transcriptomic and Epigenomic Assessment Reveals Epigenetic Regulation of WRKY Genes in Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection in Rice
- PMID: 36777006
- PMCID: PMC9878826
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202923666220510195910
Transcriptomic and Epigenomic Assessment Reveals Epigenetic Regulation of WRKY Genes in Response to Magnaporthe oryzae Infection in Rice
Abstract
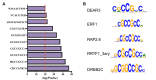
Background: Histone acetylations acting as active hallmarks for gene transcription is involved in regulating numerous developmental and stress-responsive gene expression. Methods: The data from chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) was performed by using histone H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9ac) antibody, and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) utilizing rice seedlings inoculated by Magnaporthe oryzae (M. oryzae) were integrated. Results: RNA-seq data revealed that 422, 460 and 466 genes were up-regulated at 12h, 24h and 48h after inoculation. ChIP-seq data showed that 60%-80% of blast up-regulated genes at different time points were marked with H3K9ac, which was prone to be enriched in both TSS and gene body region. However, the H3K9ac level at a rather small proportion of the up-regulated genes was elevated after M. oryzae inoculation. We found that seven WRKY genes induced by rice blast fungus harbor H3K9ac. For different WRKY genes, blast fungus induction led to the increase of H3K9ac in distinct regions, including promoter, TSS or gene body, indicating that histone acetylation may play diverse roles in the activation of defense-related genes. By searching DNA-binding motifs of transcription factors in the promoter of genes with increased H3K9ac after M. oryzae infection, we found that ERF family protein-binding motifs were enriched with high -log P-value (>20), including ERF1, DEAR3, DREB2C, RAP2.6, RRTF1_3ARY, all of which contain GCC-box (GCCGCC). Conclusion: In this study, we revealed that the vast majority of genes induced by fungus M. oryzae were marked with H3K9ac preferring both TSS and gene body regions. However, H3K9ac enrichment was increased, responding to M. oryzae inoculation only at a low proportion of these genes, including several WRKY genes. Besides, for different genes, the increment of H3K9ac occurred in different regions. Finally, ERF proteins that have been proved to bind GCC-box might be one of the potential transcription factors for recruiting histone acetyltransferases to deposit histone acetylation at defense-related genes in rice.
Keywords: ERF; H3K9ac; Magnaporthe oryzae; Rice; WRKY; histone acetylation.
© 2022 Bentham Science Publishers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances rice immunity by derepressing the expression of defense-related genes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 2;13:1041095. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1041095. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36407628 Free PMC article.
-
MoSnt2-dependent deacetylation of histone H3 mediates MoTor-dependent autophagy and plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae.Autophagy. 2018;14(9):1543-1561. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1458171. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29929416 Free PMC article.
-
Rice responds to Spodoptera frugiperda infestation via epigenetic regulation of H3K9ac in the jasmonic acid signaling and phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathways.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Feb 23;43(3):78. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03160-8. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38393406
-
The Mediator Subunit OsMED16 Interacts with the WRKY Transcription Factor OsWRKY45 to Enhance Rice Resistance Against Magnaporthe oryzae.Rice (N Y). 2024 Apr 1;17(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12284-024-00698-9. Rice (N Y). 2024. PMID: 38558163 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiling of rice early response to Magnaporthe oryzae identified OsWRKYs as important regulators in rice blast resistance.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059720. Epub 2013 Mar 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23544090 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic modulation of fungal pathogens: a focus on Magnaporthe oryzae.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 28;15:1463987. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1463987. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39529673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted roles of WRKY transcription factors in abiotic stress and flavonoid biosynthesis.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Dec 15;14:1303667. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1303667. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 38169626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances rice immunity by derepressing the expression of defense-related genes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 2;13:1041095. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1041095. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36407628 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
