Impacts of stress hyperglycemia ratio on early neurological deterioration and functional outcome after endovascular treatment in patients with acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 36777360
- PMCID: PMC9910688
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1094353
Impacts of stress hyperglycemia ratio on early neurological deterioration and functional outcome after endovascular treatment in patients with acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background and purpose: Hyperglycemia has been associated with unfavorable outcome of acute ischemic stroke, but this association has not been verified in patients with endovascular thrombectomy treatment. This study aimed to assess the impact of stress hyperglycemia ratio on early neurological deterioration and favorable outcome after thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Methods: Stroke patients with endovascular thrombectomy in two comprehensive centers were enrolled. Early neurological deterioration was defined as ≥4 points increase of National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) at 24 hours after endovascular procedure. Favorable outcome was defined as modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0-2 at 90 days of stroke onset. Multivariate regression analysis was used to identify the predictors for early neurological deterioration and favorable outcome.
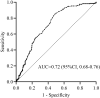
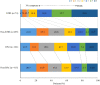
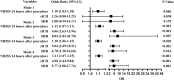
Results: Among the 559 enrolled, 74 (13.2%) patients developed early neurological deterioration. The predictors for early neurological deterioration were high stress hyperglycemia ratio at baseline (OR =5.77; 95% CI, 1.878-17.742; P =0.002), symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (OR =4.90; 95% CI, 2.439-9.835; P <0.001) and high NIHSS score after 24 hours (OR =1.11; 95% CI, 1.071-1.151; P <0.001). The predictors for favorable outcome were stress hyperglycemia ratio (OR =0.196, 95% CI, 0.077-0.502; P =0.001), age (OR =0.942, 95% CI, 0.909-0.977; P =0.001), NIHSS score 24 hours after onset (OR =0.757, 95% CI =0.693-0.827; P <0.001), groin puncture to recanalization time (OR =0.987, 95% CI, 0.975-0.998; P =0.025), poor collateral status before treatment (ASITN/SIR grade 0-3, OR =62.017, 95% CI, 25.920-148.382; P <0.001), successful recanalization (mTICI 2b or 3, OR =7.415, 95% CI, 1.942-28.313; P =0.001).
Conclusion: High stress hyperglycemia ratio may be related to early neurological deterioration and decreased likelihood of favourable outcomes after endovascular thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; early neurological deterioration; endovascular thrombectomy; large artery occlusion; stress hyperglycemia ratio.
Copyright © 2023 Dai, Cao, Wang, Li, Guo, Zhang, Jiang, Zhu, Jiang, Liu and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The association between stress hyperglycemia ratio and outcome of patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing endovascular treatment].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Jul 19;102(27):2096-2102. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20211214-02788. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35844111 Chinese.
-
Predictors of unexplained early neurological deterioration after thrombectomy for posterior circulation infarction: a reanalysis of the BASILAR study.J Neurosurg. 2024 Jun 21;141(6):1705-1711. doi: 10.3171/2024.4.JNS232632. Print 2024 Dec 1. J Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 38905713
-
Incidence and mechanism of early neurological deterioration after endovascular thrombectomy.J Neurol. 2019 Mar;266(3):609-615. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-09173-0. Epub 2019 Jan 10. J Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30631916
-
Endovascular thrombectomy and intra-arterial interventions for acute ischaemic stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 14;6(6):CD007574. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007574.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34125952 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the stress hyperglycemia ratio and clinical outcomes in patients with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 1;13:999536. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.999536. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36119678 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk factors and a model for prognosis prediction after intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase in acute ischemic stroke based on propensity score matching.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024 Jan-Dec;38:3946320241274231. doi: 10.1177/03946320241274231. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39167070 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of diabetes status and glucose measures with outcomes after endovascular therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke: an analysis of the nationwide TREAT-AIS registry.Front Neurol. 2024 May 15;15:1351150. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1351150. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38813247 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of triglyceride-glucose index combined with stress hyperglycemia ratio for all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with stroke.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Aug 18;24(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02901-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40826360 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Hyperglycemia Ratio and Hemoglobin to RDW Ratio in Predicting the Outcomes of Thrombolysis-Treated Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2025 Aug 7;13(1):e65. doi: 10.22037/aaemj.v13i1.2730. eCollection 2025. Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40801061 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between cardiometabolic indices and the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Apr 25;23(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02228-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38664793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. . Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart Association/American stroke association. Stroke (2019) 50:e344–418. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Turc G, Bhogal P, Fischer U, Khatri P, Lobotesis K, Mazighi M, et al. . European Stroke organisation (ESO) - European society for minimally invasive neurological therapy (ESMINT) guidelines on mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischaemic stroke endorsed by stroke alliance for Europe (SAFE). Eur Stroke J (2019) 4:6–12. doi: 10.1177/2396987319832140 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

