Targeted delivery of Dbait by an artificial extracellular vesicle for improved radiotherapy sensitivity of esophageal cancer
- PMID: 36777519
- PMCID: PMC9906089
Targeted delivery of Dbait by an artificial extracellular vesicle for improved radiotherapy sensitivity of esophageal cancer
Abstract
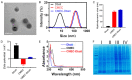
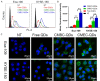
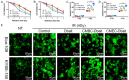
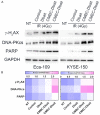
Intensification of radiotherapy has been shown to be an effective way for improving the therapeutic efficacy of radiation sensitive malignancies such as esophageal cancer (EC). The application of DNA Bait (Dbait), a type of DNA repair inhibitor, is an emerging strategy for radiosensitization. In this study, a Eca-109 cancerous cytomembrane-cloaked biomimetic drug delivery system (DDS), CMEC-Dbait, was designed and successfully fabricated, for targeted delivery of Dbait. Our systematic evaluation demonstrated that the ingenious artificial gastrointestinal extracellular vesicle owns neat spherical structure, proper particle size (154.6±5.5 nm) and surface charge (2.6±0.3 mV), favourable biocompatibility and immunocompatibility, being conducive to in vivo drug delivery. Besides, Eca-109 cytomembrane coating endowed CMEC-Dbait with effective targeting ability to homologous EC cells. Owing to these advantages, the biomimetic DDS was proved to be a potent radiosensitizer in vitro, indicated by remarkably reduced cell viability and enhanced cellular apoptosis by the combination therapy of radiation and CMEC-Dbait. The result was validated in vivo using mouse xenograft models of EC, the results illustrated that radiotherapy plus CMEC-Dbait significantly suppressed tumor growth and prolonged survival of tumor bearing mice. Western blotting results showed that CMEC-Dbait can significantly inhibit DNA damage repair signaling pathways by simulating DNA double-strand breaks both in and ex vivo. In conclusion, the versatile biomimetic CMEC-Dbait was characterized of low toxicity, excellent biocompatibility and satisfactory drug delivery efficiency, which is confirmed to be an ideal radiosensitizer for homologous cancer and merits further investigation in both pre-clinical and clinical studies.
Keywords: Dbait; Esophageal cancer; artificial gastrointestinal extracellular vesicle; biomimetic drug delivery system; radiosensitivity.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle formulation of small DNA molecules, Dbait, improves the sensitivity of hormone-independent prostate cancer to radiotherapy.Nanomedicine. 2016 Nov;12(8):2261-2271. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2016.06.010. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27389144
-
Development of a Hypoxic Radiosensitizer-Prodrug Liposome Delivery DNA Repair Inhibitor Dbait Combination with Radiotherapy for Glioma Therapy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2017 Jun;6(12). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601377. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. PMID: 28371526
-
A preclinical study combining the DNA repair inhibitor Dbait with radiotherapy for the treatment of melanoma.Neoplasia. 2014 Oct 23;16(10):835-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.08.008. eCollection 2014 Oct. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25379020 Free PMC article.
-
[Dbait: An innovative concept to inhibit DNA repair and treat cancer].Bull Cancer. 2016 Mar;103(3):227-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2016.01.007. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Bull Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26917468 Review. French.
-
D-bait: A siDNA for regulation of DNA-protein kinases against DNA damage and its implications in cancer.Int J Pharm. 2025 Mar 30;673:125416. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125416. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40024452 Review.
Cited by
-
A multifunctional targeted nano-delivery system with radiosensitization and immune activation in glioblastoma.Radiat Oncol. 2024 Sep 12;19(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02511-9. Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39267113 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-based nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 10;14:1296091. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1296091. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38660132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Yin-Yang philosophy" for the design of anticancer drug delivery nanoparticles.Biomater Transl. 2024 Jun 28;5(2):144-156. doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2024.02.005. eCollection 2024. Biomater Transl. 2024. PMID: 39351167 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
