Sesquiterpene lactones-enriched fractions from Xanthium mongolicum Kitag alleviate RA by regulating M1 macrophage polarization via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 36778009
- PMCID: PMC9909009
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1104153
Sesquiterpene lactones-enriched fractions from Xanthium mongolicum Kitag alleviate RA by regulating M1 macrophage polarization via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway
Abstract
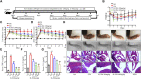
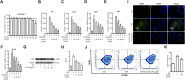
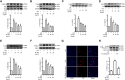
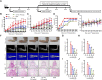
Introduction: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease, characterized by activated M1-like macrophage in the joint. Xanthium mongolicum Kitag (X. mongolicum) is a traditional medicinal plant that has long been used to treat RA and other immune diseases in China. Methods: Fractions of X. mongolicum were separated based on polarity. Anti-RA activity of the fractions were screened by LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophage in vitro. The major active compounds were identified by UPLC-MS and quantified by HPLC. The anti-RA effects of the active fraction was evaluated in complete freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis and collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse models in vivo and LPS-stimulated macrophage in vitro. Results: Sesquiterpene lactones-enriched fraction from X. mongolicum (SL-XM) exhibited the strongest anti-RA activity among all components in vitro. Five major constituents i.e., Xanthinosin (1), Xanthatin (2), Mogolide D (3), Mogolide E (4), and Mogolide A (5) were identified as major compounds of SL-XM. SL-XM ameliorated symptoms of CFA and CIA induced arthritis mice model. Furthermore, SL-XM treatment inhibited LPS-induced M1 macrophages polarization. In addition, SL-XM inhibited the phosphorylation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-induced macrophage and CIA-challenged mice. Discussion: The main anti-RA active fraction of X. mongolicum may be the Sesquiterpene lactones, which includes five key compounds. SL-XM may exert its anti-RA effect by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization via the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway.
Keywords: Xanthium mongolicum kitag; macrophage; rheumatoid arthritis; sesquiterpene lactone; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Han, Wang, Wang, Zhu, Zhang, Wu, Meng, Zhao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brenner M., Meng H. C., Yarlett N. C., Griffiths M. M., Remmers E. F., Wilder R. L., et al. (2005). The non-major histocompatibility complex quantitative trait locus Cia10 contains a major arthritis gene and regulates disease severity, pannus formation, and joint damage. Arthritis Rheum. 52 (1), 322–332. 10.1002/art.20782 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Calabresi E., Petrelli F., Bonifacio A. F., Puxeddu I., Alunno A. (2018). One year in review 2018: Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 36 (2), 175–184. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

