Multi-ancestry meta-analysis of asthma identifies novel associations and highlights the value of increased power and diversity
- PMID: 36778051
- PMCID: PMC9903683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2022.100212
Multi-ancestry meta-analysis of asthma identifies novel associations and highlights the value of increased power and diversity
Abstract
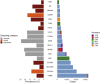
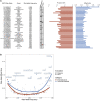
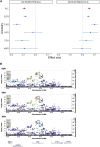
Asthma is a complex disease that varies widely in prevalence across populations. The extent to which genetic variation contributes to these disparities is unclear, as the genetics underlying asthma have been investigated primarily in populations of European descent. As part of the Global Biobank Meta-analysis Initiative, we conducted a large-scale genome-wide association study of asthma (153,763 cases and 1,647,022 controls) via meta-analysis across 22 biobanks spanning multiple ancestries. We discovered 179 asthma-associated loci, 49 of which were not previously reported. Despite the wide range in asthma prevalence among biobanks, we found largely consistent genetic effects across biobanks and ancestries. The meta-analysis also improved polygenic risk prediction in non-European populations compared with previous studies. Additionally, we found considerable genetic overlap between age-of-onset subtypes and between asthma and comorbid diseases. Our work underscores the multi-factorial nature of asthma development and offers insight into its shared genetic architecture.
Keywords: GWAS; asthma; cross-trait; heterogeneity; meta-analysis; multi-ancestry; polygenic risk prediction; subtypes.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.D. is a founder of Maze Therapeutics. B.M.N. is a member of the scientific advisory board at Deep Genomics and consultant for Camp4 Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Biogen.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multi-ancestry meta-analysis identifies 5 novel loci for ischemic stroke and reveals heterogeneity of effects between sexes and ancestries.Cell Genom. 2023 Jun 19;3(8):100345. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100345. eCollection 2023 Aug 9. Cell Genom. 2023. PMID: 37601974 Free PMC article.
-
Brugada syndrome in Japan and Europe: a genome-wide association study reveals shared genetic architecture and new risk loci.Eur Heart J. 2024 Jul 9;45(26):2320-2332. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae251. Eur Heart J. 2024. PMID: 38747976
-
Genomic predictors of combat stress vulnerability and resilience in U.S. Marines: A genome-wide association study across multiple ancestries implicates PRTFDC1 as a potential PTSD gene.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015 Jan;51:459-71. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.10.017. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25456346
-
Interpretation of risk loci from genome-wide association studies of Alzheimer's disease.Lancet Neurol. 2020 Apr;19(4):326-335. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30435-1. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Lancet Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31986256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
African American ancestry contribution to asthma and atopic dermatitis.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019 May;122(5):456-462. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2019.02.009. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30772392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Missing regulatory effects and viral triggers explored for childhood-onset asthma.Cell Genom. 2024 Sep 11;4(9):100652. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2024.100652. Cell Genom. 2024. PMID: 39265526 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Inflammation in Asthma: Looking Beyond the Th2 Cell.Immunol Rev. 2025 Mar;330(1):e70010. doi: 10.1111/imr.70010. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40016948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation as a possible mechanism linking childhood adversity and health: results from a 2-sample mendelian randomization study.Am J Epidemiol. 2024 Nov 4;193(11):1541-1552. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwae072. Am J Epidemiol. 2024. PMID: 38754872 Free PMC article.
-
Serum microRNA expression quantitative trait loci in children with asthma colocalize with asthma-related GWAS results.NPJ Genom Med. 2025 Jul 17;10(1):55. doi: 10.1038/s41525-025-00510-7. NPJ Genom Med. 2025. PMID: 40676019 Free PMC article.
-
Powerful mapping of cis-genetic effects on gene expression across diverse populations reveals novel disease-critical genes.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 26:2024.09.25.24314410. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.25.24314410. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39399015 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Moffatt M.F., Gut I.G., Demenais F., Strachan D.P., Bouzigon E., Heath S., von Mutius E., Farrall M., Lathrop M., Cookson W.O.C.M., GABRIEL Consortium A large-scale, consortium-based genomewide association study of asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;363:1211–1221. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0906312. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

