Development of artificial neural network models to predict the PAMPA effective permeability of new, orally administered drugs active against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36778642
- PMCID: PMC9901841
- DOI: 10.1007/s13721-023-00410-9
Development of artificial neural network models to predict the PAMPA effective permeability of new, orally administered drugs active against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
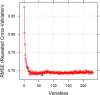
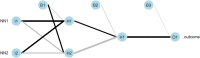
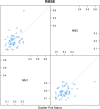
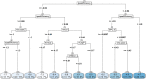
Responding to the pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2, the scientific community intensified efforts to provide drugs effective against the virus. To strengthen these efforts, the "COVID Moonshot" project has been accepting public suggestions for computationally triaged, synthesized, and tested molecules. The project aimed to identify molecules of low molecular weight with activity against the virus, for oral treatment. The ability of a drug to cross the intestinal cell membranes and enter circulation decisively influences its bioavailability, and hence the need to optimize permeability in the early stages of drug discovery. In our present work, as a contribution to the ongoing scientific efforts, we employed artificial neural network algorithms to develop QSAR tools for modelling the PAMPA effective permeability (passive diffusion) of orally administered drugs. We identified a set of 61 features most relevant in explaining drug cell permeability and used them to develop a stacked regression ensemble model, subsequently used to predict the permeability of molecules included in datasets made available through the COVID Moonshot project. Our model was shown to be robust and may provide a promising framework for predicting the potential permeability of molecules not yet synthesized, thus guiding the process of drug design.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13721-023-00410-9.
Keywords: Artificial neural network; COVID-19; Descriptors; Ensemble modelling; PAMPA; Permeability.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Development and validation of PAMPA-BBB QSAR model to predict brain penetration potential of novel drug candidates.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 1;14:1291246. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1291246. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38108064 Free PMC article.
-
Parallel artificial membrane permeability assay (PAMPA) combined with a 10-day multiscreen Caco-2 cell culture as a tool for assessing new drug candidates.Pharmazie. 2008 Mar;63(3):194-9. Pharmazie. 2008. PMID: 18444507
-
In Silico Prediction of PAMPA Effective Permeability Using a Two-QSAR Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 28;20(13):3170. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133170. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261723 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Molecular Treatments.Curr Mol Med. 2022;22(7):621-639. doi: 10.2174/1566524021666211013121831. Curr Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34645374 Review.
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-Analysis of Permeability Literature Data Shows Possibilities and Limitations of Popular Methods.Mol Pharm. 2025 Mar 3;22(3):1293-1304. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00975. Epub 2025 Feb 20. Mol Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39977255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alex A, Millan DS, Perez M, et al. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding to improve membrane permeability and absorption in beyond rule of five chemical space. Med Chem Commun. 2011;2:669–674. doi: 10.1039/C1MD00093D. - DOI
-
- Alloqmani, A., B., Y., Irshad, A., Alsolami, F. Deep learning based anomaly detection in images: Insights, challenges and recommendations. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2021, 12. 10.14569/IJACSA.2021.0120428
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
