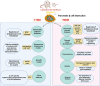
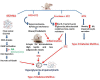
Rodent models for diabetes
- PMID: 36778766
- PMCID: PMC9908807
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03488-0
Rodent models for diabetes
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with many health complications and is potentially a morbid condition. As prevalence increases at an alarming rate around the world, research into new antidiabetic compounds with different mechanisms is the top priority. Therefore, the preclinical experimental induction of DM is imperative for advancing knowledge, understanding pathogenesis, and developing new drugs. Efforts have been made to examine recent literature on the various induction methods of Type I and Type II DM. The review summarizes the different in vivo models of DM induced by chemical, surgical, and genetic (immunological) manipulations and the use of pathogens such as viruses. For good preclinical assessment, the animal model must exhibit face, predictive, and construct validity. Among all reported models, chemically induced DM with streptozotocin was found to be the most preferred model. However, the purpose of the research and the outcomes to be achieved should be taken into account. This review was aimed at bringing together models, benefits, limitations, species, and strains. It will help the researcher to understand the pathophysiology of DM and to choose appropriate animal models.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Hyperglycemia; Insulin resistance; Streptozotocin.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental Animal Models: Tools to Investigate Antidiabetic Activity.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(2):79-94. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221220115649. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 36545714 Review.
-
Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Neonatal Rats: An Insight into its Applications to Induce Diabetic Complications.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;16(1):26-39. doi: 10.2174/1573399815666190411115829. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019. PMID: 30973111 Review.
-
Experimental Models to Study Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications: Limitations and New Opportunities.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 18;24(12):10309. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210309. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A 50-year history of new drugs in Japan-the development and progress of anti-diabetic drugs and the epidemiological aspects of diabetes mellitus].Yakushigaku Zasshi. 2003;38(1):11-27. Yakushigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14570054 Japanese.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Preclinical Diabetic Models.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020;16(2):104-116. doi: 10.2174/1573399815666190510112035. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020. PMID: 31074371
Cited by
-
Animal Models in Diabetic Research-History, Presence, and Future Perspectives.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 20;11(10):2852. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102852. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy through modulating mitochondrial biogenesis and suppressing oxidative stress.World J Diabetes. 2025 Feb 15;16(2):93130. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i2.93130. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39959279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkandahri MY, Sujana D, Hasyim DM, Shafirany MZ, Sulastri L, et al. Antidiabetic activity of extract and fractions of castanopsis costata leaves on alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacogn J. 2021;13(6):1589–1593. doi: 10.5530/pj.2021.13.204. - DOI
-
- Arulmozhi DK, Veeranjaneyulu A, Bodhankar SL. Neonatal streptozotocin-induced rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a glance. Indian J Pharmacol. 2004;36(4):217–221.
-
- Arya A, Jamil Al-Obaidi MM, Karim RB, Taha H, Khan AK, et al. Extract of Woodfordia fruticosa flowers ameliorates hyperglycemia, oxidative stress and improves β-cell function in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;175:229–240. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.057. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aswar U, Patil R, Bodhankar S. Short review on the induction of obesity in laboratory animals. Diabesity. 2019;5(4):25–31. doi: 10.15562/diabesity.2019.58. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

