Therapeutic efficacy of liraglutide versus metformin in modulating the gut microbiota for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 36778868
- PMCID: PMC9909237
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1088187
Therapeutic efficacy of liraglutide versus metformin in modulating the gut microbiota for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
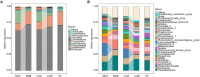
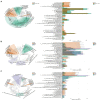
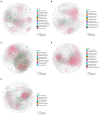
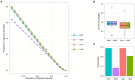
Metformin and liraglutide are used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) complicated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Although these drugs can alter the intestinal microbiome, clinical data are required to explore their mechanisms of action. Using 16S sequencing technology, we analyzed and compared the intestinal bacterial community structure and function between patients before and after treatment (12 weeks) with the two drugs (metformin or liraglutide, n = 15) and healthy controls (n = 15). Moreover, combined with 19 clinical indices, the potential therapeutic mechanisms of the two drugs were compared. The studied clinical indices included those associated with islet β-cell function (FPG, FINS, HbA1c, and HOMA-IR), inflammation (TNF-α, IL-6, and APN), lipid metabolism (TC, TG, and LDL-C), and liver function (ALT, AST, and GGT); the values of all indices changed significantly after treatment (p < 0.01). In addition, the effect of the two drugs on the intestinal bacterial community varied. Liraglutide treatment significantly increased the diversity and richness of the intestinal bacterial community (p < 0.05); it significantly increased the relative abundances of Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Bacilli, whereas metformin treatment significantly increased the relative abundance of Fusobacteria and Actinobacteria (p < 0.05). Metformin treatment increased the complexity and stability of the intestinal bacterial network. However, liraglutide treatment had a weaker effect on the intestinal bacterial network, and the network after treatment was similar to that in healthy controls. Correlation matrix analysis between dominant genera and clinical indicators showed that the correlation between the bacterial community and islet β-cell function was stronger after liraglutide treatment, whereas the correlation between the bacterial community and inflammation-related factors was stronger after metformin treatment. Functional prediction showed that liraglutide could significantly affect the abundance of functional genes related to T2DM and NAFLD (p < 0.05), but the effect of metformin was not significant. This study is the first to report the changes in the intestinal bacterial community in patients treated with metformin or liraglutide and the differences between the mechanisms of action of metformin and liraglutide. Metformin or liraglutide has a therapeutic value in T2DM complicated with NAFLD, with liraglutide having a weaker effect on the intestinal bacterial community but a better therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: NAFLD; T2DM; intestinal microorganism; liraglutide; metformin.
Copyright © 2023 Ying, Rongjiong, Kahaer, Chunhui and Wulasihan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of liraglutide in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Biosci Rep. 2018 Dec 21;38(6):BSR20181304. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181304. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30473540 Free PMC article.
-
Liraglutide or insulin glargine treatments improves hepatic fat in obese patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in twenty-six weeks: A randomized placebo-controlled trial.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Dec;170:108487. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108487. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 33035599 Clinical Trial.
-
Liraglutide modulates gut microbiome and attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver in db/db mice.Life Sci. 2020 Nov 15;261:118457. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118457. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32961235
-
Diabetes drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review.Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 29;8(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s13643-019-1200-8. Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31783920 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of metformin on nonalcoholic fatty liver based on meta-analysis and network pharmacology.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 28;101(43):e31437. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031437. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36316840 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Current Background, Hopes, and Perspectives.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 23;13(5):581. doi: 10.3390/metabo13050581. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37233622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined effects of Yupingfeng and metformin on blood glucose levels and intestinal tissue in high-fat diet-induced type 2 diabetic rats.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 23;16:1532560. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1532560. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40771277 Free PMC article.
-
Rebalancing the Gut: Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Agonists as a Strategy for Obesity and Metabolic Health.Cureus. 2024 Jul 17;16(7):e64738. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64738. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39156410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between glucagon-like peptide 1 and gut microbiota in metabolic diseases.mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0203223. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02032-23. Epub 2023 Dec 6. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38055342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP-1RAs attenuated obesity and reversed leptin resistance partly via activating the microbiome-derived inosine/A2A pathway.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Feb;15(2):1023-1038. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.006. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40177547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad A., Ali T., Kim M. W., Khan A., Jo M. H., Rehman S. U., et al. . (2019). Adiponectin homolog novel osmotin protects obesity/diabetes-induced NAFLD by upregulating AdipoRs/PPARα signaling in Ob/Ob and db/db transgenic mouse models. Metab. Clin. Exp. 90, 31–43. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.10.004, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Budoff M. J., Davis T. M. E., Palmer A. G., Frederich R., Lawrence D. E., Liu J., et al. . (2021). Efficacy and safety of Ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by metformin and sulfonylurea: a sub-study of VERTIS CV. Diabetes Ther. 12, 1279–1297. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01033-x, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

