Molecular and Therapeutic Insights of Alpha-Lipoic Acid as a Potential Molecule for Disease Prevention
- PMID: 36778891
- PMCID: PMC9904877
- DOI: 10.1007/s43450-023-00370-1
Molecular and Therapeutic Insights of Alpha-Lipoic Acid as a Potential Molecule for Disease Prevention
Abstract
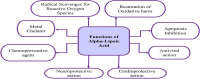
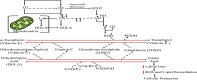
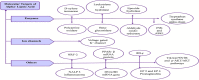
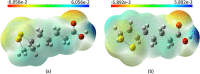
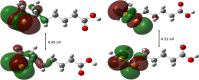
Alpha-lipoic acid is an organic, sulfate-based compound produced by plants, humans, and animals. As a potent antioxidant and a natural dithiol compound, it performs a crucial role in mitochondrial bioenergetic reactions. A healthy human body, on the other hand, can synthesize enough α-lipoic acid to scavenge reactive oxygen species and increase endogenous antioxidants; however, the amount of α-lipoic acid inside the body decreases significantly with age, resulting in endothelial dysfunction. Molecular orbital energy and spin density analysis indicate that the sulfhydryl (-SH) group of molecules has the greatest electron donating activity, which would be responsible for the antioxidant potential and free radical scavenging activity. α-Lipoic acid acts as a chelating agent for metal ions, a quenching agent for reactive oxygen species, and a reducing agent for the oxidized form of glutathione and vitamins C and E. α-Lipoic acid enantiomers and its reduced form have antioxidant, cognitive, cardiovascular, detoxifying, anti-aging, dietary supplement, anti-cancer, neuroprotective, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. α-Lipoic acid has cytotoxic and antiproliferative effects on several cancers, including polycystic ovarian syndrome. It also has usefulness in the context of female and male infertility. Although α-lipoic acid has numerous clinical applications, the majority of them stem from its antioxidant properties; however, its bioavailability in its pure form is low (approximately 30%). However, nanoformulations have shown promise in this regard. The proton affinity and electron donating activity, as a redox-active agent, would be responsible for the antioxidant potential and free radical scavenging activity of the molecule. This review discusses the most recent clinical data on α-lipoic acid in the prevention, management, and treatment of a variety of diseases, including coronavirus disease 2019. Based on current evidence, the preclinical and clinical potential of this molecule is discussed.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s43450-023-00370-1.
Keywords: Electronic structure study; Gut microbiota; Molecular targets; Neuroprotection; Pharmacological potential; Thioctic acid.
© The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Sociedade Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Physiological effect and therapeutic application of alpha lipoic acid.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(32):3636-45. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140706141806. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25005184 Review.
-
Alpha-lipoic Acid: An Antioxidant with Anti-aging Properties for Disease Therapy.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(1):23-54. doi: 10.2174/0109298673300496240416114827. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38644711 Review.
-
The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid.Gen Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;29(3):315-31. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(96)00474-0. Gen Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9378235 Review.
-
Diabetes and alpha lipoic Acid.Front Pharmacol. 2011 Nov 17;2:69. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2011.00069. eCollection 2011. Front Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22125537 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum-chemical investigation of the structure and the antioxidant properties of α-lipoic acid and its metabolites.J Mol Model. 2012 Jul;18(7):2907-16. doi: 10.1007/s00894-011-1306-y. Epub 2011 Nov 30. J Mol Model. 2012. PMID: 22127611 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protective Effect of Lipoic Acid on Oxidative Stress and Tissue Damage Induced by Aflatoxin B1 in Young Laying Hens.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Apr 6;17(4):184. doi: 10.3390/toxins17040184. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40278682 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in α-Lipoic Acid for Disease Prevention: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Insights.Molecules. 2025 Apr 29;30(9):1972. doi: 10.3390/molecules30091972. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40363779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Addressing the Challenges and Complexities Surrounding a 70-Year-Old Compound.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 May 29;47(6):402. doi: 10.3390/cimb47060402. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of alpha-lipoic acid transdermal patch for local subcutaneous fat reduction: A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial in overweight volunteers.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024 Nov 24;42:101402. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2024.101402. eCollection 2024 Dec. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024. PMID: 39678156 Free PMC article.
-
Microemulsions Improve the Cutaneous Co-Localization of Lipoic Acid and Quercetin and Antioxidant Effects in Cutaneous Cells and Tissue.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Feb 26;26(3):70. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03062-2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40011308
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
