ADRB2 Regulates the Proliferation and Metastasis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells by Enhancing the ETV1-c-KIT Signaling
- PMID: 36778918
- PMCID: PMC9918370
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6413796
ADRB2 Regulates the Proliferation and Metastasis of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells by Enhancing the ETV1-c-KIT Signaling
Abstract
Background: Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) originates from a pacemaker cell, the Cajal cell. However, little is known about the cancer neuroscience in GIST. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the clinical and biological roles of adrenoceptor beta 2 (ADRB2) in GIST.
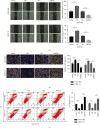
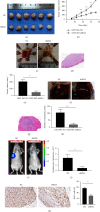
Methods: Immunohistochemistry was used to evaluate the expression of ADRB2 in GIST tissues. The biological effects of ADRB2 on GIST cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis were explored using Cell Counting Kit -8, plate colony formation assay, transwell invasion assay, and flow cytometry. We also explored the growth and metastasis of xenograft tumors in nude mice. Western blotting was used to quantify protein expression and phosphorylation.
Results: ADRB2 is generally highly expressed in GIST. High ADRB2 expression was significantly associated with risk level, tumor size, mitotic count, and metastasis. Overexpression of ADRB2 promoted GIST cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis, while silencing ADRB2 expression showed the opposite effects. Furthermore, we found that silencing endogenous ADRB2 inhibited GIST progression and metastasis in nude mice. ADRB2-induced ETV1 upregulation enhanced the activation of c-KIT.
Conclusion: ADRB2 plays an important role in the proliferation and metastasis of GIST and is expected to be a potential target for the treatment of GIST.
Copyright © 2023 Sijun Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor-α Regulates Proliferation of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells With Mutations in KIT by Stabilizing ETV1.Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug;149(2):420-32.e16. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.006. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25865047 Free PMC article.
-
TATA-box-binding protein-associated factor 15 is a novel biomarker that promotes cell proliferation and migration in gastrointestinal stromal tumor.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 May 21;29(19):2932-2949. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i19.2932. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37274797 Free PMC article.
-
KIT Exon 11 Codons 557-558 Deletion Mutation Promotes Liver Metastasis Through the CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 15;22(14):3477-87. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2748. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26936919
-
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) pathogenesis, familial GIST, and animal models.Semin Diagn Pathol. 2006 May;23(2):63-9. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2006.08.003. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2006. PMID: 17193819 Review.
-
Pathology of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Pathol Int. 2006 Jan;56(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2006.01924.x. Pathol Int. 2006. PMID: 16398673 Review.
Cited by
-
PEA3 Transcription Factors, Role in Invasion, Proliferation and Radioresistance of Glioblastoma Stem Cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Apr;29(8):e70533. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70533. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40275610 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

