Integrating LASSO Feature Selection and Soft Voting Classifier to Identify Origins of Replication Sites
- PMID: 36778978
- PMCID: PMC9878833
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202923666220214122506
Integrating LASSO Feature Selection and Soft Voting Classifier to Identify Origins of Replication Sites
Abstract
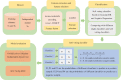
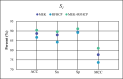
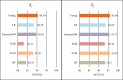
Background: DNA replication plays an indispensable role in the transmission of genetic information. It is considered to be the basis of biological inheritance and the most fundamental process in all biological life. Considering that DNA replication initiates with a special location, namely the origin of replication, a better and accurate prediction of the origins of replication sites (ORIs) is essential to gain insight into the relationship with gene expression. Objective: In this study, we have developed an efficient predictor called iORI-LAVT for ORIs identification. Methods: This work focuses on extracting feature information from three aspects, including mono-nucleotide encoding, k-mer and ring-function-hydrogen-chemical properties. Subsequently, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) as a feature selection is applied to select the optimal features. Comparing the different combined soft voting classifiers results, the soft voting classifier based on GaussianNB and Logistic Regression is employed as the final classifier. Results: Based on 10-fold cross-validation test, the prediction accuracies of two benchmark datasets are 90.39% and 95.96%, respectively. As for the independent dataset, our method achieves high accuracy of 91.3%. Conclusion: Compared with previous predictors, iORI-LAVT outperforms the existing methods. It is believed that iORI-LAVT predictor is a promising alternative for further research on identifying ORIs.
Keywords: DNA replication; LASSO; Origin of replication sites; dimensional feature; multi-feature; voting classifier.
© 2022 Bentham Science Publishers.
Figures


References
-
- Raghu Ram E.V., Kumar A., Biswas S., Kumar A., Chaubey S., Siddiqi M.I., Habib S. Nuclear gyrB encodes a functional subunit of the Plasmodium falciparum gyrase that is involved in apicoplast DNA replication. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007;154(1):30–39. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2007.04.001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
