Identifying vulnerable plaques: A 3D carotid plaque radiomics model based on HRMRI
- PMID: 36779063
- PMCID: PMC9908750
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1050899
Identifying vulnerable plaques: A 3D carotid plaque radiomics model based on HRMRI
Abstract
Background: Identification of vulnerable carotid plaque is important for the treatment and prevention of stroke. In previous studies, plaque vulnerability was assessed qualitatively. We aimed to develop a 3D carotid plaque radiomics model based on high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (HRMRI) to quantitatively identify vulnerable plaques.
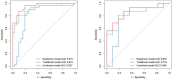
Methods: Ninety patients with carotid atherosclerosis who underwent HRMRI were randomized into training and test cohorts. Using the radiological characteristics of carotid plaques, a traditional model was constructed. A 3D carotid plaque radiomics model was constructed using the radiomics features of 3D T1-SPACE and its contrast-enhanced sequences. A combined model was constructed using radiological and radiomics characteristics. Nomogram was generated based on the combined models, and ROC curves were utilized to assess the performance of each model.
Results: 48 patients (53.33%) were symptomatic and 42 (46.67%) were asymptomatic. The traditional model was constructed using intraplaque hemorrhage, plaque enhancement, wall remodeling pattern, and lumen stenosis, and it provided an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.816 vs. 0.778 in the training and testing sets. In the two cohorts, the 3D carotid plaque radiomics model and the combined model had an AUC of 0.915 vs. 0.835 and 0.957 vs. 0.864, respectively. In the training set, both the radiomics model and the combination model outperformed the traditional model, but there was no significant difference between the radiomics model and the combined model.
Conclusions: HRMRI-based 3D carotid radiomics models can improve the precision of detecting vulnerable carotid plaques, consequently improving risk classification and clinical decision-making in patients with carotid stenosis.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; carotid atherosclerosis (AS); high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging; radiomics; stroke; vulnerable plaque.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Hua, Chen, Jiao, Shan, Li and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chaturvedi S, Bruno A, Feasby T, Holloway R, Benavente O, Cohen SN, et al. Carotid endarterectomy–an evidence-based review: report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. (2005) 65:794–801. 10.1212/01.wnl.0000176036.07558.82 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

