Computational Investigation of a Series of Small Molecules as Potential Compounds for Lysyl Hydroxylase-2 (LH2) Inhibition
- PMID: 36779232
- PMCID: PMC10233724
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01448
Computational Investigation of a Series of Small Molecules as Potential Compounds for Lysyl Hydroxylase-2 (LH2) Inhibition
Abstract
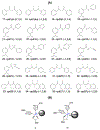
The catalytic function of lysyl hydroxylase-2 (LH2), a member of the Fe(II)/αKG-dependent oxygenase superfamily, is to catalyze the hydroxylation of lysine to hydroxylysine in collagen, resulting in stable hydroxylysine aldehyde-derived collagen cross-links (HLCCs). Reports show that high amounts of LH2 lead to the accumulation of HLCCs, causing fibrosis and specific types of cancer metastasis. Some members of the Fe(II)/αKG-dependent family have also been reported to have intramolecular O2 tunnels, which aid in transporting one of the required cosubstrates into the active site. While LH2 can be a promising target to combat these diseases, efficacious inhibitors are still lacking. We have used computational simulations to investigate a series of 44 small molecules as lead compounds for LH2 inhibition. Tunneling analyses indicate the existence of several intramolecular tunnels. The lengths of the calculated O2-transporting tunnels in holoenzymes are relatively longer than those in the apoenzyme, suggesting that the ligands may affect the enzyme's structure and possibly block (at least partially) the tunnels. The sequence alignment analysis between LH enzymes from different organisms shows that all of the amino acid residues with the highest occurrence rate in the oxygen tunnels are conserved. Our results suggest that the enolate form of diketone compounds establishes stronger interactions with the Fe(II) in the active site. Branching the enolate compounds with functional groups such as phenyl and pyridinyl enhances the interaction with various residues around the active site. Our results provide information about possible leads for further LH2 inhibition design and development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): PR is the co-founder of Qubit Pharmaceuticals.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Development of a High-Throughput Lysyl Hydroxylase (LH) Assay and Identification of Small-Molecule Inhibitors against LH2.SLAS Discov. 2019 Apr;24(4):484-491. doi: 10.1177/2472555218817057. Epub 2018 Dec 27. SLAS Discov. 2019. PMID: 30589612 Free PMC article.
-
Lysyl Hydroxylase 2 Is Secreted by Tumor Cells and Can Modify Collagen in the Extracellular Space.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 9;291(50):25799-25808. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.759803. Epub 2016 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27803159 Free PMC article.
-
A scalable lysyl hydroxylase 2 expression system and luciferase-based enzymatic activity assay.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Mar 15;618:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28216326 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen cross-linking mediated by lysyl hydroxylase 2: an enzymatic battlefield to combat fibrosis.Essays Biochem. 2019 Sep 13;63(3):377-387. doi: 10.1042/EBC20180051. Print 2019 Sep 13. Essays Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31324706 Review.
-
Expanding the lysyl hydroxylase toolbox: new insights into the localization and activities of lysyl hydroxylase 3 (LH3).J Cell Physiol. 2007 Aug;212(2):323-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21036. J Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17516569 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of the Inhibition Mechanism of Xanthine Oxidoreductase by Oxipurinol: A Computational Study.J Chem Inf Model. 2023 Jul 10;63(13):4190-4206. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c00624. Epub 2023 Jun 15. J Chem Inf Model. 2023. PMID: 37319436 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Extracellular Matrix Crosslinking as a Therapeutic Approach to Fibrosis.Cells. 2024 Mar 2;13(5):438. doi: 10.3390/cells13050438. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging therapeutic targets in systemic sclerosis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2024 Apr;102(4):465-478. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02424-w. Epub 2024 Feb 22. J Mol Med (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38386070 Review.
-
Computational studies on the functional and structural impact of pathogenic mutations in enzymes.Protein Sci. 2025 Apr;34(4):e70081. doi: 10.1002/pro.70081. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40116283 Review.
-
Unleashing the Potential of 1,3-Diketone Analogues as Selective LH2 Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Sep 22;14(10):1396-1403. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00305. eCollection 2023 Oct 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 37849534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loenarz C; Schofield CJ Expanding chemical biology of 2-oxoglutarate oxygenases. Nat. Chem. Biol 2008, 4, 152–156. - PubMed
-
- Hausinger RP Fe (II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases and related enzymes. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol 2004, 39, 21–68. - PubMed
-
- Flashman E; Schofield CJ The most versatile of all reactive intermediates? Nat. Chem. Biol 2007, 3, 86–87. - PubMed
-
- Hautala T; Byers MG; Eddy RL; Shows TB; Kivirikko KI; Myllyla R Cloning of human lysyl hydroxylase: Complete cDNA-derived amino acid sequence and assignment of the gene (PLOD) to chromosome 1p36. 3→ p36. 2. Genomics 1992, 13, 62–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

