Mutations in rpoB That Confer Rifampicin Resistance Can Alter Levels of Peptidoglycan Precursors and Affect β-Lactam Susceptibility
- PMID: 36779708
- PMCID: PMC10128067
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.03168-22
Mutations in rpoB That Confer Rifampicin Resistance Can Alter Levels of Peptidoglycan Precursors and Affect β-Lactam Susceptibility
Abstract
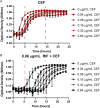
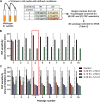
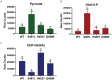
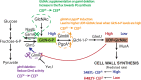
Bacteria can adapt to stressful conditions through mutations affecting the RNA polymerase core subunits that lead to beneficial changes in transcription. In response to selection with rifampicin (RIF), mutations arise in the RIF resistance-determining region (RRDR) of rpoB that reduce antibiotic binding. These changes can also alter transcription and thereby have pleiotropic effects on bacterial fitness. Here, we studied the evolution of resistance in Bacillus subtilis to the synergistic combination of RIF and the β-lactam cefuroxime (CEF). Two independent evolution experiments led to the recovery of a single rpoB allele (S487L) that was able to confer resistance to RIF and CEF through a single mutation. Two other common RRDR mutations made the cells 32 times more sensitive to CEF (H482Y) or led to only modest CEF resistance (Q469R). The diverse effects of these three mutations on CEF resistance are correlated with differences in the expression of peptidoglycan (PG) synthesis genes and in the levels of two metabolites crucial in regulating PG synthesis, glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcN-6-P) and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc). We conclude that RRDR mutations can have widely varying effects on pathways important for cell wall biosynthesis, and this may restrict the spectrum of mutations that arise during combination therapy. IMPORTANCE Rifampicin (RIF) is one of the most valued drugs in the treatment of tuberculosis. TB treatment relies on a combination therapy and for multidrug-resistant strains may include β-lactams. Mutations in rpoB present a common route for emergence of resistance to RIF. In this study, using B. subtilis as a model, we evaluate the emergence of resistance for the synergistic combination of RIF and the β-lactam cefuroxime (CEF). One clinically relevant rpoB mutation conferred resistance to both RIF and CEF, whereas one other increased CEF sensitivity. We were able to link these CEF sensitivity phenotypes to accumulation of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc), which feedback regulates GlmS activity and thereby peptidoglycan synthesis. Further, we found that higher CEF concentrations precluded the emergence of high RIF resistance. Collectively, these results suggest that multidrug treatment regimens may limit the available pathways for the evolution of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; RNA polymerases; antibiotic resistance; antibiotic synergy; metabolomics; peptidoglycan; rifampicin; β-lactams.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rifampicin resistance mutations in the 81 bp RRDR of rpoB gene in Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates using Xpert MTB/RIF in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan: a retrospective study.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 12;16:413. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1745-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27519406 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling and identification of novel rpoB mutations in rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates from Pakistan.J Infect Chemother. 2021 Nov;27(11):1578-1583. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2021.06.020. Epub 2021 Jul 7. J Infect Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34244055
-
Reevaluating Rifampicin Breakpoint Concentrations for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates with Disputed rpoB Mutations and Discordant Susceptibility Phenotypes.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0208721. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02087-21. Epub 2022 Feb 2. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35107324 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations inside rifampicin-resistance determining region of rpoB gene associated with rifampicin-resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Infect Public Health. 2018 Sep-Oct;11(5):605-610. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 26. J Infect Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29706316 Review.
-
Association between the rifampicin resistance mutations and rifabutin susceptibility in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A meta-analysis.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2025 Jan;40:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2024.11.014. Epub 2024 Nov 29. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2025. PMID: 39617268 Review.
Cited by
-
8-OxoG-Dependent Regulation of Global Protein Responses Leads to Mutagenesis and Stress Survival in Bacillus subtilis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 8;13(3):332. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030332. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539865 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation in RNA polymerase imparts resistance to β-lactams by preventing dysregulation of amino acid and nucleotide metabolism.Cell Rep. 2025 Feb 25;44(2):115268. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115268. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 39908144 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing analysis to identify antimicrobial resistance regions and virulence factors in Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from the Amhara Region, Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2025 May 8;15(1):16076. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01241-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40341578 Free PMC article.
-
A dose-response model for statistical analysis of chemical genetic interactions in CRISPRi screens.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 May 20;20(5):e1011408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011408. eCollection 2024 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38768228 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-Specific Effects of Mutations in the Rifampin Resistance-Determining Region (RRDR) of RpoB on Physiology and Antibiotic Resistance in Enterococcus faecium.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Aug 4:2025.07.25.666922. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.25.666922. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40799600 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Storz G, Hengge R. 2011. Bacterial stress responses, 2nd ed. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
-
- LaCroix RA, Sandberg TE, O'Brien EJ, Utrilla J, Ebrahim A, Guzman GI, Szubin R, Palsson BO, Feist AM. 2015. Use of adaptive laboratory evolution to discover key mutations enabling rapid growth of Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 on glucose minimal medium. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:17–30. doi:10.1128/AEM.02246-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kuehne SA, Dempster AW, Collery MM, Joshi N, Jowett J, Kelly ML, Cave R, Longshaw CM, Minton NP. 2018. Characterization of the impact of rpoB mutations on the in vitro and in vivo competitive fitness of Clostridium difficile and susceptibility to fidaxomicin. J Antimicrob Chemother 73:973–980. doi:10.1093/jac/dkx486. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
